Page 204 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 204
Unit-9: Theory of Cost and Revenue
cost curve. Long-term average cost curve is inverted J-shaped, because with the increase in the Notes
production cost of production decreases.
According to the modern theory, the cost relating to the data available, it certainly cannot be based on
the long-term average cost curve is L-shaped or inverted J-shaped. But it can certainly be said that LAC,
is not U shaped. It is U-shaped when it will be in a position to produce high-scale production may suffer
losses. But in real life scale to production scale of losses is not high.
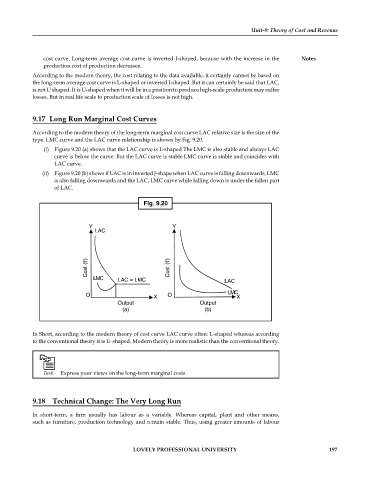
9.17 Long Run Marginal Cost Curves
According to the modern theory of the long-term marginal cost curve LAC relative size is the size of the
type. LMC curve and the LAC curve relationship is shown by Fig. 9.20.
(i) Figure 9.20 (a) shows that the LAC curve is L-shaped The LMC is also stable and always LAC
curve is below the curve. But the LAC curve is stable LMC curve is stable and coincides with
LAC curve.
(ii) Figure 9.20 (b) shows if LAC is in inverted J-shape when LAC curve is falling downwards, LMC
is also falling downwards and the LAC, LMC curve while falling down is under the fallen part
of LAC.
Fig. 9.20
Y Y
LAC
Cost (`) Cost (`)
LMC LAC = LMC LAC
LMC
O X O X
Output Output
(a) (b)
In Short, according to the modern theory of cost curve LAC curve often: L-shaped whereas according
to the conventional theory it is U-shaped. Modern theory is more realistic than the conventional theory.
Express your views on the long-term marginal costs.
9.18 Technical Change: The Very Long Run
In short-term, a firm usually has labour as a variable. Whereas capital, plant and other means,
such as furniture, production technology and remain stable. Thus, using greater amounts of labour
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 197