Page 203 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 203
Microeconomic Theory
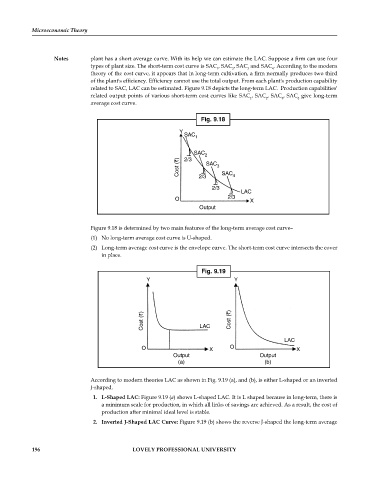
Notes plant has a short average curve. With its help we can estimate the LAC. Suppose a firm can use four
types of plant size. The short-term cost curve is SAC , SAC , SAC and SAC . According to the modern
3
4
1
2
theory of the cost curve, it appears that in long-term cultivation, a firm normally produces two third
of the plant's efficiency. Efficiency cannot use the total output. From each plant's production capability
related to SAC, LAC can be estimated. Figure 9.18 depicts the long-term LAC. Production capabilities'
related output points of various short-term cost curves like SAC , SAC , SAC , SAC give long-term
2
1
3
4
average cost curve.
Fig. 9.18
Y
SAC
1
SAC
2
Cost (`) 2/3 SAC 3 SAC 4
2/3
2/3
LAC
O 2/3 X
Output
Figure 9.18 is determined by two main features of the long-term average cost curve–
(1) No long-term average cost curve is U-shaped.
(2) Long-term average cost curve is the envelope curve. The short-term cost curve intersects the cover
in place.
Fig. 9.19
Y Y
Cost (`) LAC Cost (`)
LAC
O X O X
Output Output
(a) (b)
According to modern theories LAC as shown in Fig. 9.19 (a), and (b), is either L-shaped or an inverted
J-shaped.
1. L-Shaped LAC: Figure 9.19 (a) shows L-shaped LAC. It is L shaped because in long-term, there is
a minimum scale for production, in which all links of savings are achieved. As a result, the cost of
production after minimal ideal level is stable.
2. Inverted J-Shaped LAC Curve: Figure 9.19 (b) shows the reverse J-shaped the long-term average
196 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY