Page 191 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 191
Microeconomic Theory
Notes In Table 6, the average variable cost and average fixed cost is estimated by adding the average cost.
Seventh unit is less than the average cost. Because the average fixed and average variable costs are also
reduced. Seventh unit has the lowest average cost, average cost is increasing because the AVC is also
increasing.
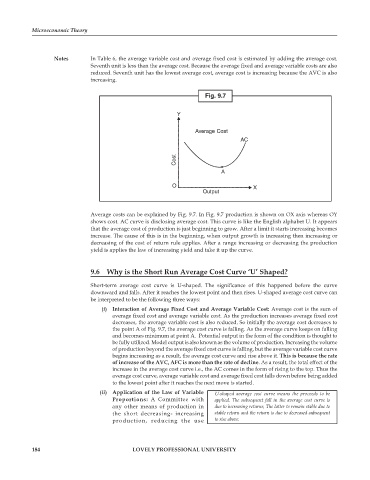
Fig. 9.7
Y
Average Cost
AC
Cost
A
O X
Output
Average costs can be explained by Fig. 9.7. In Fig. 9.7 production is shown on OX axis whereas OY
shows cost. AC curve is disclosing average cost. This curve is like the English alphabet U. It appears
that the average cost of production is just beginning to grow. After a limit it starts increasing becomes
increase. The cause of this is in the beginning, when output growth is increasing then increasing or
decreasing of the cost of return rule applies. After a range increasing or decreasing the production
yield is applies the law of increasing yield and take it up the curve.
9.6 Why is the Short Run Average Cost Curve ‘U’ Shaped?
Short-term average cost curve is U-shaped. The significance of this happened before the curve
downward and falls. After it reaches the lowest point and then rises. U-shaped average cost curve can
be interpreted to be the following three ways:
(i) Interaction of Average Fixed Cost and Average Variable Cost: Average cost is the sum of
average fixed cost and average variable cost. As the production increases average fixed cost
decreases, the average variable cost is also reduced. So initially the average cost decreases to
the point A of Fig. 9.7, the average cost curve is falling. As the average curve keeps on falling
and becomes minimum at point A. Potential output in the form of the condition is thought to
be fully utilized. Model output is also known as the volume of production. Increasing the volume
of production beyond the average fixed cost curve is falling, but the average variable cost curve
begins increasing as a result, the average cost curve and rise above it. This is because the rate
of increase of the AVC, AFC is more than the rate of decline. As a result, the total effect of the
increase in the average cost curve i.e., the AC comes in the form of rising to the top. Thus the
average cost curve, average variable cost and average fixed cost falls down before being added
to the lowest point after it reaches the next move is started.
(ii) Application of the Law of Variable U-shaped average cost curve means the proceeds to be
Proportions: A Committee with applied. The subsequent fall in the average cost curve is
any other means of production in due to increasing returns, The latter to remain stable due to
the short decreasing- increasing stable return and the return is due to decreased subsequent
production, reducing the use to rise above.
184 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY