Page 296 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 296
Unit-16: Duopoly and Oligopoly: Cournot Model and Kinked Demand Curve
Notes
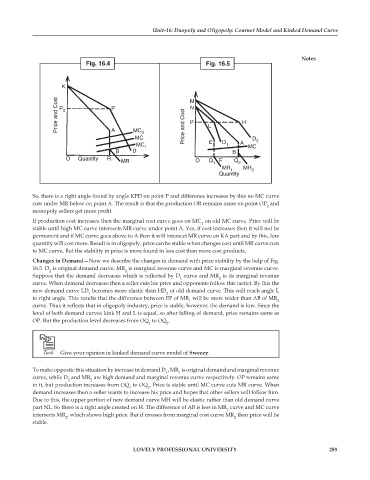
Fig. 16.4 Fig. 16.5
K
Price and Cost P 0 P M L H
N
P
A
MC
MC 2 Price and Cost D 2
MC 1 E D 1 A MC
B D B
O Quantity R
MR O Q 1 F Q 2
MR 1 MR 2
Quantity
So, there is a right angle found by angle KPD on point P and difference increases by this no MC curve
cuts under MR below on point A. The result is that the production OR remains same on point OP and
0
monopoly sellers get more profit.
If production cost increases then the marginal cost curve goes on MC on old MC curve. Price will be
2
stable until high MC curve intersects MR curve under point A. Yes, if cost increases then it will not be
permanent and if MC curve goes above to A then it will intersect MR curve on KA part and by this, low
quantity will cost more. Result is in oligopoly, price can be stable when changes cost until MR curve cuts
to MC curve. But the stability in price is more found in less cost than more cost products.
Changes in Demand—Now we describe the changes in demand with price stability by the help of Fig.
16.5. D is original demand curve, MR is marginal revenue curve and MC is marginal revenue curve.
2
2
Suppose that the demand decreases which is reflected by D curve and MR is its marginal revenue
1
1
curve. When demand decreases then a seller cuts his price and opponents follow this tactict. By this the
new demand curve LD becomes more elastic than HD of old demand curve. This will reach angle L
2
1
to right angle. This results that the difference between EF of MR will be more wider than AB of MR
1
2
curve. Thus it reflects that in oligopoly industry, price is stable, however, the demand is low. Since the
level of both demand curves kink H and L is equal, so after falling of demand, price remains same as
OP. But the production level decreases from OQ to OQ .
1
2
Give your opinion in kinked demand curve model of Sweezy.
To make opposite this situation by increase in demand D , MR is original demand and marginal revenue
1
1
curve, while D and MR are high demand and marginal revenue curve respectively. OP remains same
2
2
in it, but production increases from OQ to OQ . Price is stable until MC curve cuts MR curve. When
2
1
demand increases then a seller wants to increase his price and hopes that other sellers will follow him.
Due to this, the upper portion of new demand curve MH will be elastic rather than old demand curve
part NL. So there is a right angle created on H. The difference of AB is less in MR curve and MC curve
2
intersects MR , which shows high price. But if crosses from marginal cost curve MR then price will be
2
2
stable.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 289