Page 303 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 303
Microeconomic Theory
Notes 1. Price Constant
In this condition, entrant firm expects constant price after entry level. Established firms permit entrant
firms to fix the price of the quantity of commodity on given demand curve and plant scale of this firm.
As a result, less will be the parts in total production of established firms.
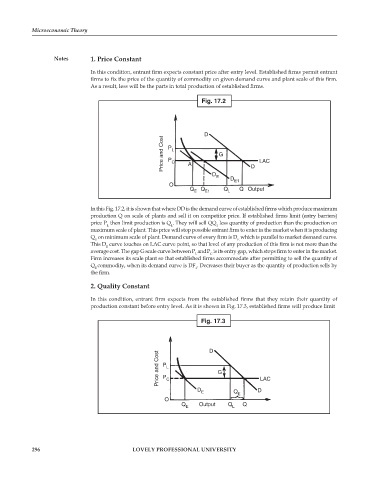
Fig. 17.2
D
Price and Cost P L C A G LAC
P
D D
E
D E1
O
Q Q Q Q Output
E E1 L
In this Fig. 17.2, it is shown that where DD is the demand curve of established firms which produce maximum
production Q on scale of plants and sell it on competitor price. If established firms limit (entry barriers)
price P then limit production is Q . They will sell QQ less quantity of production than the production on
L
1
L
maximum scale of plant. This price will stop possible entrant firm to enter in the market when it is producing
Q on minimum scale of plant. Demand curve of every firm is D which is parallel to market demand curve.
E
E
This D curve touches on LAC curve point, so that level of any production of this firm is not more than the
E
average cost. The gap G scale curve between P andP is its entry gap, which stops firm to enter in the market.
L C
Firm increases its scale plant so that established firms accommodate after permitting to sell the quantity of
Q commodity, when its demand curve is DF . Decreases their buyer as the quantity of production sells by
1
E
the firm.
2. Quality Constant
In this condition, entrant firm expects from the established firms that they retain their quantity of
production constant before entry level. As it is shown in Fig. 17.3, established firms will produce limit
Fig. 17.3
Price and Cost P L C D G LAC
P
D D
E Q
E
O
Q Output Q Q
E L
296 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY