Page 310 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 310
Unit-18: Profit Maximization and Full Cost Pricing Theories
Notes
Fig. 18.1
Revenue/Cost A B MC AR
= MR
OM M
1
Output
Profit Maximization Under Monopoly
In the monopoly the firm itself is the seller (or producer) of a product. Therefore, its demand curve is
sloping down from right. It is assumed that interests and habits are given. It is the price maker and it
decides the maximum price and maximum profit. But it does not mean that it can fix both the price
and quantity of production. If the firm makes the level of production, so its price is decided by marked
demand. Or if it decides the price, so the production level will depend upon the demand of product by
consumer. However, in any situation, the monopoly firms have only aims to maximize the profit. The
condition of monopoly is (1) MR = MR < AR (price), and (2) MR curve is cut by MC curve from down.
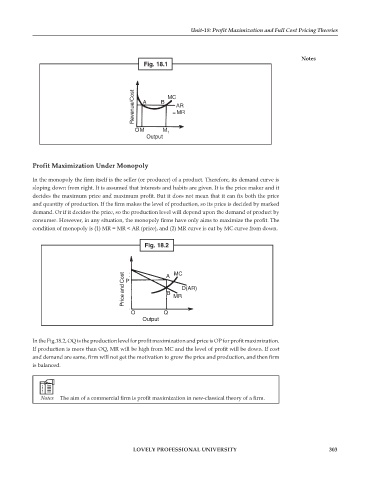
Fig. 18.2
MC
Price and Cost P A MR D(AR)
B
O Q
Output
In the Fig.18.2, OQ is the production level for profit maximization and price is OP for profit maximization.
If production is more than OQ, MR will be high from MC and the level of profit will be down. If cost
and demand are same, firm will not get the motivation to grow the price and production, and then firm
is balanced.
The aim of a commercial firm is profit maximization in new-classical theory of a firm.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 303