Page 314 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 314
Unit-18: Profit Maximization and Full Cost Pricing Theories
Cost rise or cost decision boundary formula is, Notes
P – AVC
M = ________ So, P = AVC (1 + M)
.
AVC
Where, M is increased value, P is price and AVC is average substitution cost.
Suppose AVC of firm is = 100 and firm M = 0.25 or 25%. Firm will decide, price P, 100 (1 + 0.25) = 125.
When this price is chosen by the form whatever its prodoction, then mark-up should be constant. But
there will be still possibility of changes in mark-up (M) by the direct sources of production.
Depending on the firm capacity and available factors of production (wages and raw material), there
is no possibility of change, whether the production level is anything. On that price, firm will sell the
quantity demanded by customer.
But how the production level is decided? This is decided in any manner from these three—(a) percentage
of production capacity or (b) in the form of last sold production in its production time period or average
production which is to be sold in future. If a firm is new or starting a new product first and third point
will be noted. This may be possible first will be match with third because the capacity of plant will
depend upon possible sells in future.
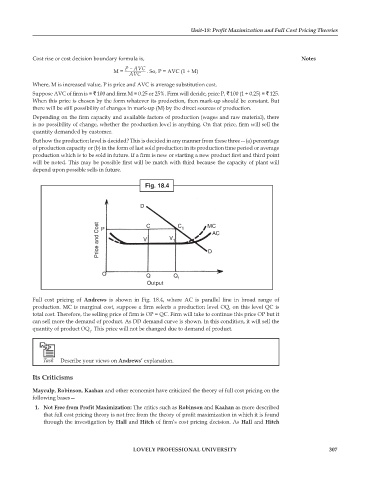
Fig. 18.4
D
Price and Cost P V C V 1 C 1 MC
AC
D
O Q Q
1
Output
Full cost pricing of Andrews is shown in Fig. 18.4, where AC is parallel line in broad range of
production. MC is marginal cost, suppose a firm selects a production level OQ, on this level QC is
total cost. Therefore, the selling price of firm is OP = QC. Firm will take to continue this price OP but it
can sell more the demand of product. As DD demand curve is shown. In this condition, it will sell the
quantity of product OQ . This price will not be changed due to demand of product.
1
Describe your views on Andrews’ explanation.
Its Criticisms
Mayculp, Robinson, Kaahan and other economist have criticized the theory of full cost pricing on the
following bases—
1. Not Free from Profit Maximization: The critics such as Robinson and Kaahan as more described
that full cost pricing theory is not free from the theory of profit maximization in which it is found
through the investigation by Hall and Hitch of firm’s cost pricing decision. As Hall and Hitch
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 307