Page 80 - DECO401_MICROECONOMIC_THEORY_ENGLISH
P. 80
Unit-4: Ordinal Utility Theory: Indifference Curve Approach
oranges is OM and for apples is OQ. Consumer is in equilibrium on point P where budget line MQ is Notes
touching the indifference curve IC. It means that consumer will buy the quantity of apple OA. Let’s
assume that the price of apple falls. Hence the budget line will go rightward as compared to price
falls and it will now MQ as compared to MQ. This will touch the new indifference curve IC to point
1
1
P . So the new equilibrium point would be P . Consumer will now buy OC quantity of apple. The
1
1
combination of P, P and P is called Price Consumption Curve. This curve represents the effect of
2
1
change in behaviour of consumer if the price of apple changes. The Price Consumption Curve is the
curve which gives figure about the quantity of apples or product buys by consumer if the income and
the price of other products remain stable.
4.29 Slope of PCC Curve
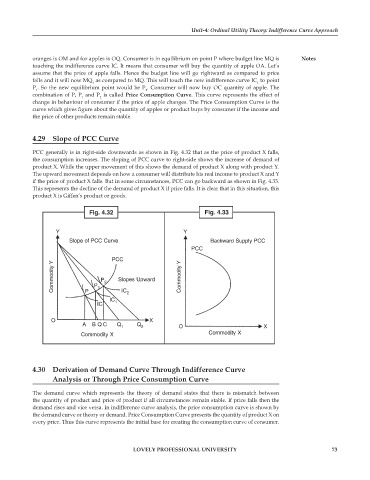
PCC generally is in right-side downwards as shown in Fig. 4.32 that as the price of product X falls,
the consumption increases. The sloping of PCC curve to right-side shows the increase of demand of
product X. While the upper movement of this shows the demand of product X along with product Y.
The upward movement depends on how a consumer will distribute his real income to product X and Y
if the price of product X falls. But in some circumstances, PCC can go backward as shown in Fig. 4.33.
This represents the decline of the demand of product X if price falls. It is clear that in this situation, this
product X is Giffen’s product or goods.
Fig. 4.32 Fig. 4.33
Y Y
Slope of PCC Curve Backward Supply PCC
PCC
PCC
Commodity Y P 2 Slopes Upward Commodity Y
P
1
IC
P
2
IC 1
IC
O X
A B QC Q Q
1 2 O X
Commodity X Commodity X
4.30 Derivation of Demand Curve Through Indifference Curve
Analysis or Through Price Consumption Curve
The demand curve which represents the theory of demand states that there is mismatch between
the quantity of product and price of product if all circumstances remain stable. If price falls then the
demand rises and vice versa. In indifference curve analysis, the price consumption curve is shown by
the demand curve or theory or demand. Price Consumption Curve presents the quantity of product X on
every price. Thus this curve represents the initial base for creating the consumption curve of consumer.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 73