Page 236 - DECO402_Macro Economics
P. 236
Unit-26: Kaldor’s Theory of Trade Cycle Contents
S = f (Y, K) Notes
I = f (Y, K)
dS > 0, dS > 0
IY dK
dI > 0, dI < 0
dY dK
dI dS
And, dY > dY
In other words, in contraction phase, MPI > MPS
The above relations show that S and I directly change positively with Y. S changes directly with K
and Y changes inversely with K.
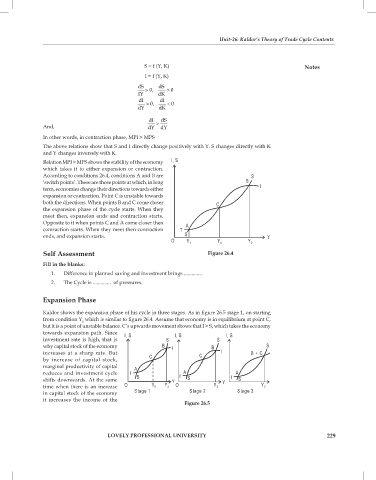
Relation MPI > MPS shows the stability of the economy
which takes it to either expansion or contraction.
According to conditions 26.4, conditions A and B are
‘switch points’. These are those points at which, in long
term, economies change their directions towards either
expansion or contraction. Point C is unstable towards
both the directions. When points B and C come closer
the expansion phase of the cycle starts. When they
meet then, expansion ends and contraction starts.
Opposite to it when points C and A come closer then
contraction starts. When they meet then contraction
ends, and expansion starts.
Self Assessment Figure 26.4
Fill in the blanks:
1. Difference in planned saving and investment brings ..............
2. The Cycle is .............. of pressures.
Expansion Phase
Kaldor shows the expansion phase of his cycle in three stages. As in figure 26.5 stage 1, on starting
from condition Y which is similar to figure 26.4. Assume that economy is in equilibrium at point C,
0
but it is a point of unstable balance. C’s upwards movement shows that I > S, which takes the economy
towards expansion path. Since
investment rate is high, that is
why capital stock of the economy
increases at a sharp rate. But
by increase of capital stock,
marginal productivity of capital
reduces and investment cycle
shifts downwards. At the same
time when there is an increase
in capital stock of the economy
it increases the income of the
Figure 26.5
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 229