Page 64 - DECO402_Macro Economics
P. 64
Unit-6: Keynesian Theory of Employment
So, Aggregate demand can describe as the get currency in exchange of that things and services of Notes
firms, which are produced in fixed number by labour.
When firms want to earn more by increasing expenditure on services or society, they provide
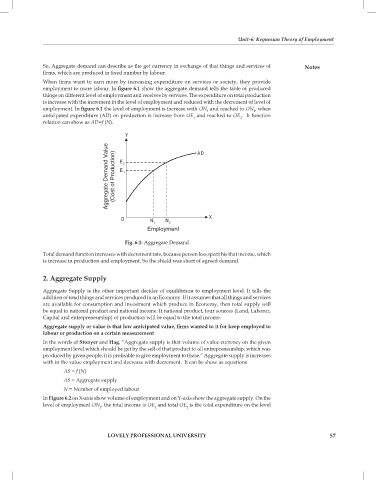
employment to more labour. In figure 6.1 show the aggregate demand tells the table of produced
things on different level of employment and receives by services. The expenditure on total production
is increase with the increment in the level of employment and reduced with the decrement of level of
employment. In figure 6.1 the level of employment is increase with ON and reached to ON , when
2
1
anticipated expenditure (AD) on production is increase from OE and reached to OE . It function
1
2
relation can show as AD=f (N).
Aggregate Demand Value (Cost of Production)
Employment
Fig. 6.1: Aggregate Demand
Total demand function increases with decrement rate, because person less spent his that income, which
is increase in production and employment. So the shield was short of agreed demand.
2. Aggregate Supply
Aggregate Supply is the other important decider of equilibrium to employment level. It tells the
addition of total things and services produced in an Economy. If it assumes that all things and services
are available for consumption and investment which produce in Economy, then total supply will
be equal to national product and national income. It national product, four sources (Land, Laborur,
Capital and entrepreneurship) of production will be equal to the total income.
Aggregate supply or value is that low anticipated value, firms wanted to it for keep employed to
labour or production on a certain measurement
In the words of Stonyer and Hag, “Aggregate supply is that volume of value currency on the given
employment level which should be get by the sell of that product to all entrepreneurship, which was
produced by given people, it is profitable to give employment to those.” Aggregate supply is increases
with in the value employment and decrease with decrement. It can be show as equations
AS = f (N)
AS = Aggregate supply
N = Number of employed labour
In Figure 6.2 on X-axis show volume of employment and on Y-axis show the aggregate supply. On the
level of employment ON , the total income is OE and total OE is the total expenditure on the level
1 1 2
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 57