Page 101 - DECO502_INDIAN_ECONOMIC_POLICY_ENGLISH
P. 101
Unit 9: Inflation: Nature and Extent
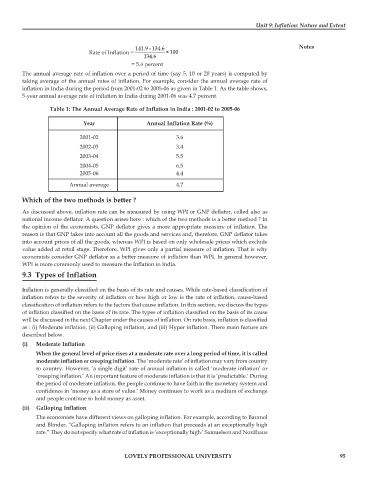
141.9 - 134.6 Notes
Rate of Inflation = ×100
134.6
= 5.4 percent
The annual average rate of inflation over a period of time (say 5, 10 or 20 years) is computed by
taking average of the annual rates of inflation. For example, consider the annual average rate of
inflation in India during the period from 2001-02 to 2005-06 as given in Table 1. As the table shows,
5-year annual average rate of inflation in India during 2001-06 was 4.7 percent.
Table 1: The Annual Average Rate of Inflation in India : 2001-02 to 2005-06
Year Annual Inflation Rate (%)
2001-02 3.6
2002-03 3.4
2003-04 5.5
2004-05 6.5
2005-06 4.4
Annual average 4.7
Which of the two methods is better ?
As discussed above, inflation rate can be measured by using WPI or GNP deflator, called also as
national income deflator. A question arises here : which of the two methods is a better method ? In
the opinion of the economists, GNP deflator gives a more appropriate measure of inflation. The
reason is that GNP takes into account all the goods and services and, therefore, GNP deflator takes
into account prices of all the goods, whereas WPI is based on only wholesale prices which exclude
value added at retail stage. Therefore, WPI gives only a partial measure of inflation. That is why
economists consider GNP deflator as a better measure of inflation than WPI. In general however,
WPI is more commonly used to measure the Inflation in India.
9.3 Types of Inflation
Inflation is generally classified on the basis of its rate and causes. While rate-based classification of
inflation refers to the severity of inflation or how high or low is the rate of inflation, cause-based
classification of inflation refers to the factors that cause inflation. In this section, we discuss the types
of inflation classified on the basis of its rate. The types of inflation classified on the basis of its cause
will be discussed in the next Chapter under the causes of inflation. On rate basis, inflation is classified
as : (i) Moderate inflation, (ii) Galloping inflation, and (iii) Hyper inflation. There main feature are
described below.
(i) Moderate Inflation
When the general level of price rises at a moderate rate over a long period of time, it is called
moderate inflation or creeping inflation. The ‘moderate rate’ of inflation may vary from country
to country. However, ‘a single digit’ rate of annual inflation is called ‘moderate inflation’ or
‘creeping inflation.’ An important feature of moderate inflation is that it is ‘predictable.’ During
the period of moderate inflation, the people continue to have faith in the monetary system and
confidence in ‘money as a store of value.’ Money continues to work as a medium of exchange
and people continue to hold money as asset.
(ii) Galloping Inflation
The economists have different views on galloping inflation. For example, according to Baumol
and Blinder, “Galloping inflation refers to an inflation that proceeds at an exceptionally high
rate.” They do not specify what rate of inflation is ‘exceptionally high.’ Samuelson and Nordhaus
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 95