Page 105 - DECO502_INDIAN_ECONOMIC_POLICY_ENGLISH
P. 105
Unit 9: Inflation: Nature and Extent
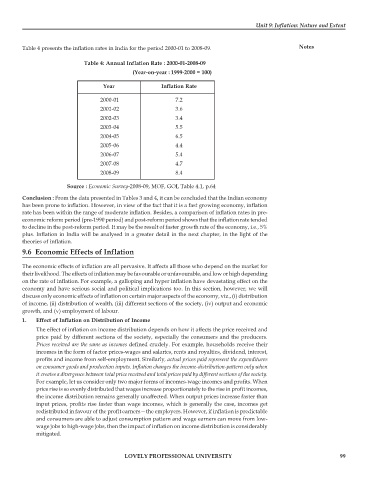
Table 4 presents the inflation rates in India for the period 2000-01 to 2008-09. Notes
Table 4: Annual Inflation Rate : 2000-01-2008-09
(Year-on-year : 1999-2000 = 100)
Year Inflation Rate
2000-01 7.2
2001-02 3.6
2002-03 3.4
2003-04 5.5
2004-05 6.5
2005-06 4.4
2006-07 5.4
2007-08 4.7
2008-09 8.4
Source : Economic Survey-2008-09, MOF, GOI, Table 4.1, p.64
Conclusion : From the data presented in Tables 3 and 4, it can be concluded that the Indian economy
has been prone to inflation. However, in view of the fact that it is a fast growing economy, inflation
rate has been within the range of moderate inflation. Besides, a comparison of inflation rates in pre-
economic reform period (pre-1990 period) and post-reform period shows that the inflation rate tended
to decline in the post-reform period. It may be the result of faster growth rate of the economy, i.e., 5%
plus. Inflation in India will be analysed in a greater detail in the next chapter, in the light of the
theories of inflation.
9.6 Economic Effects of Inflation
The economic effects of inflation are all pervasive. It affects all those who depend on the market for
their livelihood. The effects of inflation may be favourable or unfavourable, and low or high depending
on the rate of inflation. For example, a galloping and hyper inflation have devastating effect on the
economy and have serious social and political implications too. In this section, however, we will
discuss only economic effects of inflation on certain major aspects of the economy, viz., (i) distribution
of income, (ii) distribution of wealth, (iii) different sections of the society, (iv) output and economic
growth, and (v) employment of labour.
1. Effect of Inflation on Distribution of Income
The effect of inflation on income distribution depends on how it affects the price received and
price paid by different sections of the society, especially the consumers and the producers.
Prices received are the same as incomes defined crudely. For example, households receive their
incomes in the form of factor prices-wages and salaries, rents and royalties, dividend, interest,
profits and income from self-employment. Similarly, actual prices paid represent the expenditures
on consumer goods and production inputs. Inflation changes the income-distribution-pattern only when
it creates a divergence between total price received and total prices paid by different sections of the society.
For example, let us consider only two major forms of incomes-wage incomes and profits. When
price rise is so evenly distributed that wages increase proportionately to the rise in profit incomes,
the income distribution remains generally unaffected. When output prices increase faster than
input prices, profits rise faster than wage incomes, which is generally the case, incomes get
redistributed in favour of the profit earners—the employers. However, if inflation is predictable
and consumers are able to adjust consumption pattern and wage earners can move from low-
wage jobs to high-wage jobs, then the impact of inflation on income distribution is considerably
mitigated.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 99