Page 280 - DECO502_INDIAN_ECONOMIC_POLICY_ENGLISH
P. 280
Indian Economic Policy
Notes needs of specified sectors (like equipment leasing and hire purchase) are some of the factors enhancing
the attractiveness of this sector.”
Essentially, these finance companies are banks, since they perform the basic twin functions of attracting
deposits from the public and making loans. RBI again argues : “... The rapid growth of NBFCs especially
in the nineties, has led to a gradual blurring of dividing lines between banks and NBFCs, with the
exception of the exclusive privilege that commercial banks exercise in the issuance of cheques.”
Since NBFCs are not regarded as banking companies, they did not come under the control of RBI,
there is no minimum liquidity ratio or cash ratio, no specific ratio between their owned funds and
deposits. That the depositors of these companies are subject to extreme insecurity is clear from the
fact that :
(a) bulk of their loans are unsecured and are given to very risky enterprises and hence their charging
high rates of interest;
(b) the loans, though given for short periods, can be and are renewed frequently and thus become
long-term loans;
(c) as there is no exchange of communication between different companies, it is possible for a
person or party to borrow from more than one finance company; and
(d) the deposits of the public with the finance companies are not protected by the Deposit Insurance
Corporation.
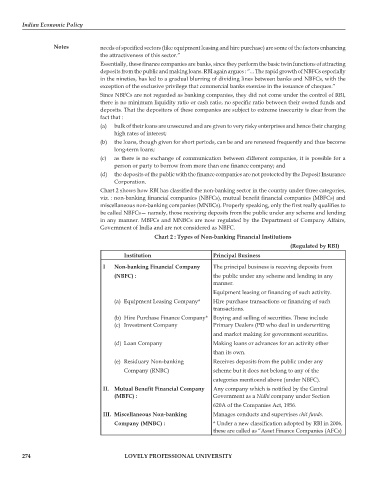
Chart 2 shows how RBI has classified the non-banking sector in the country under three categories,
viz. : non-banking financial companies (NBFCs), mutual benefit financial companies (MBFCs) and
miscellaneous non-banking companies (MNBCs). Properly speaking, only the first really qualifies to
be called NBFCs— namely, those receiving deposits from the public under any scheme and lending
in any manner. MBFCs and MNBCs are now regulated by the Department of Company Affairs,
Government of India and are not considered as NBFC.
Chart 2 : Types of Non-banking Financial Institutions
(Regulated by RBI)
Institution Principal Business
I Non-banking Financial Company The principal business is receving deposits from
(NBFC) : the public under any scheme and lending in any
manner.
Equipment leasing or financing of such activity.
(a) Equipment Leasing Company* Hire purchase transactions or financing of such
transactions.
(b) Hire Purchase Finance Company* Buying and selling of securities. These include
(c) Investment Company Primary Dealers (PD who deal in underwriting
and market making for government securities.
(d) Loan Company Making loans or advances for an activity other
than its own.
(e) Residuary Non-banking Receives deposits from the public under any
Company (RNBC) scheme but it does not belong to any of the
categories mentioend above (under NBFC).
II. Mutual Benefit Financial Company Any company which is notified by the Central
(MBFC) : Government as a Nidhi company under Section
620A of the Companies Act, 1956.
III. Miscellaneous Non-banking Manages conducts and supervises chit funds.
Company (MNBC) : * Under a new classification adopted by RBI in 2006,
these are called as “Asset Finance Companies (AFCs)
274 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY