Page 276 - DECO502_INDIAN_ECONOMIC_POLICY_ENGLISH
P. 276
Indian Economic Policy
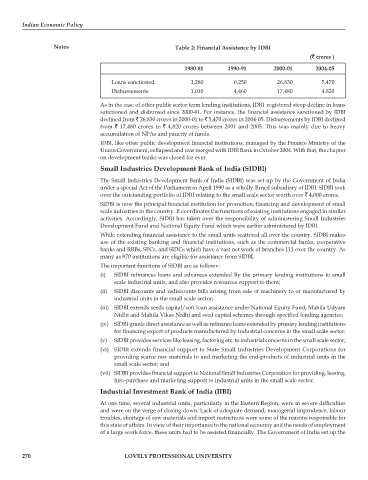
Notes Table 2: Financial Assistance by IDBI
(`` `` ` crores )
1980-81 1990-91 2000-01 2004-05
Loans sanctioned 1,280 6,250 26,830 5,470
Disbursements 1,010 4,460 17,480 4.820
As in the case of other public sector term lending institutions, IDBI registered steep decline in loans
satictioned and disbursed since 2000-01. For instance, the financial assistance sanctioned by IDBI
declined from ` 26,830 crores in 2000-01 to ` 5,470 crores in 2004-05. Disbursements by IDBI declined
from ` 17,480 crores to ` 4,820 crores between 2001 and 2005. This was mainly due to heavy
accumulation of NPAs and paucity of funds.
IDBI, like other public development financial institutions, managed by the Finance Ministry of the
Union Government, collapsed and was merged with IDBI Bank in October 2004. With that, the chapter
on development banks was closed for ever.
Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI)
The Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI) was set up by the Government of India
under a special Act of the Parliament in April 1990 as a wholly-Brned subsidiary of IDBI. SIDBI took
over the outstanding portfolio of IDBI relating to the small scale sector worth over ` 4,000 crores.
SIDBI is now the principal financial institution for promotion, financing and development of small
scale industries in the country. It coordinates the functions of existing institutions engaged in similar
activities. Accordingly, SIDBI has taken over the responsibility of administering Small Industries
Development Fund and National Equity Fund which were earlier administered by IDBI.
While extending financial assistance to the small units scattered all over the country, SIDBI makes
use of the existing banking and financial institutions, such as the commercial banks, cooperative
banks and RRBs, SFCs, and SIDCs which have a vast net work of branches 111 over the country. As
many as 870 institutions are eligible for assistance from SIDBI.
The important functions of SIDBI are as follows :
(i) SIDBI refinances loans and advances extended By the primary lending institutions to small
scale industrial units, and also provides resources support to them;
(ii) SIDBI discounts and rediscounts bills arising from sale of machinery to or manufactured by
industrial units in the small scale sector;
(iii) SIDBI extends seeds capital/soft loan assistance under National Equity Fund, Mahila Udyam
Nidhi and Mahila Vikas Nidhi and seed capital schemes through specified lending agencies;
(iv) SIDBI grants direct assistance as well as refinance loans extended by primary lending institutions
for financing export of products manufactured by Industrial concerns in the small scale sector;
(v) SIDBI provides services like leasing, factoring etc. to industrial concerns in the small scale sector;
(vi) SIDBI extends financial support to State Small Industries Development Corporations for
providing scarce raw materials to and marketing the end-products of industrial units in the
small scale sector; and
(vii) SIDBI provides financial support to National Small Industries Corporation for providing, leasing,
hire-purchase and marketing support to industrial units in the small scale sector.
Industrial Investment Bank of India (IIBI)
At one time, several industrial units, particularly in the Eastern Region, were in severe difficulties
and were on the verge of closing down. Lack of adequate demand, managerial imprudence, labour
troubles, shortage of raw materials and import restrictions were some of the reasons responsible for
this state of affairs. In view of their importance to the national economy and the needs of employment
of a large work force, these units had to be assisted financially. The Government of India set up the
270 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY