Page 264 - DECO503_INTERNATIONAL_TRADE_AND_FINANCE_ENGLISH
P. 264
International Trade and Finance
Notes 24.1 WTO (World Trade Organization)
The WTO came into existence on 1 January 1995 as successor to the General Agreements on Tariffs
and Trade (GATT). Its genesis goes back to the post-Second-World-War period in the late 1940s
when economies of most European countries and the US were greatly disrupted following the war
and the great depression of the 1930s. Consequently a United Nations Conference on Trade and
Employment was convened at Havana in November 1947. It led to an international agreement called
Havana Charter to create an International Trade Organization (ITO), a specialized agency of the
United Nations to handle the trade side of international economic cooperation. The draft ITO charter
was ambitious and extended beyond world trade discipline to rules on employment, commodity
agreements, restrictive business practices, international investment, and services. However, the attempt
to create the ITO was aborted as the US did not ratify it and other countries found it difficult to make
it operational without US support.
The combined package of trade rules and tariff concessions negotiated and agreed by 23 countries
out of 50 participating countries became known as General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT):
an effort to salvage from the aborted attempt to create the ITO. India was also a founder member of
GATT, a multilateral treaty aimed at trade liberalization. GATT provided a multilateral forum during
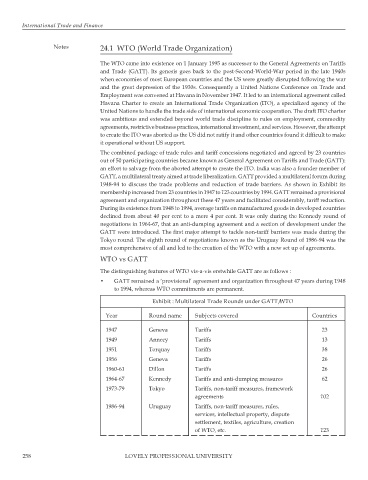
1948-94 to discuss the trade problems and reduction of trade barriers. As shown in Exhibit its
membership increased from 23 countries in 1947 to 123 countries by 1994. GATT remained a provisional
agreement and organization throughout these 47 years and facilitated considerably, tariff reduction.
During its existence from 1948 to 1994, average tariffs on manufactured goods in developed countries
declined from about 40 per cent to a mere 4 per cent. It was only during the Kennedy round of
negotiations in 1964-67, that an anti-dumping agreement and a section of development under the
GATT were introduced. The first major attempt to tackle non-tariff barriers was made during the
Tokyo round. The eighth round of negotiations known as the Uruguay Round of 1986-94 was the
most comprehensive of all and led to the creation of the WTO with a new set up of agreements.
WTO vs GATT
The distinguishing features of WTO vis-a-vis erstwhile GATT are as follows :
• GATT remained a ‘provisional’ agreement and organization throughout 47 years during 1948
to 1994, whereas WTO commitments are permanent.
Exhibit : Multilateral Trade Rounds under GATT/WTO
Year Round name Subjects covered Countries
1947 Geneva Tariffs 23
1949 Annecy Tariffs 13
1951 Torquay Tariffs 38
1956 Geneva Tariffs 26
1960-61 Dillon Tariffs 26
1964-67 Kennedy Tariffs and anti-dumping measures 62
1973-79 Tokyo Tariffs, non-tariff measures, framework
agreements 102
1986-94 Uruguay Tariffs, non-tariff measures, rules,
services, intellectual property, dispute
settlement, textiles, agriculture, creation
of WTO, etc. 123
258 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY