Page 275 - DECO504_STATISTICAL_METHODS_IN_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 275
Unit 21: Cost of Living Index and Its Uses and Limitations of Index Numbers
Example 9: (a) From the chain base index numbers given below, prepare fixed base index Notes
numbers:
Year: 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005
Index: 110 150 140 200 150
(b) From the chain base index number given below, construct fixed base index
numbers:
Year: 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005
Chain Base Indices: 80 110 120 90 140
Solution:
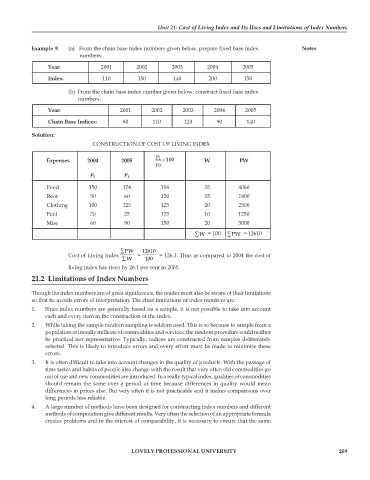
CONSTRUCTION OF COST OF LIVING INDEX
p
Expenses 2004 2005 1 × 100 W PW
p 0
p p
0 1
Food 150 174 116 35 4060
Rent 50 60 120 15 1800
Clothing 100 125 125 20 2500
Fuel 20 25 125 10 1250
Misc 60 90 150 20 3000
∑W = 100 ∑PW = 12610
∑PW 12610
Cost of Living Index = = 126.1. Thus as compared to 2004 the cost of
∑W 100
living index has risen by 26.1 per cent in 2005.
21.2 Limitations of Index Numbers
Though the index numbers are of great significance, the reader must also be aware of their limitations
so that he avoids errors of interpretation. The chief limitations of index numbers are:
1. Since index numbers are generally based on a sample, it is not possible to take into account
each and every item in the construction of the index.
2. While taking the sample random sampling is seldom used. This is so because to sample from a
population of literally millions of commodities and services, the random procedure could neither
be practical nor representative. Typically, indices are constructed from samples deliberately
selected. This is likely to introduce errors and every effort must be made to minimise these
errors.
3. It is often difficult to take into account changes in the quality of products. With the passage of
time tastes and habits of people also change with the result that very often old commodities go
out of use and new commodities are introduced. In a really typical index, qualities of commodities
should remain the same over a period of time because differences in quality would mean
differences in prices also. But very often it is not practicable and it makes comparisons over
long periods less reliable.
4. A large number of methods have been designed for constructing index numbers and different
methods of computation give different results. Very often the selection of an appropriate formula
creates problems and in the interest of comparability, it is necessary to ensure that the same
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 269