Page 323 - DECO504_STATISTICAL_METHODS_IN_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 323
Statistical Methods in Economics
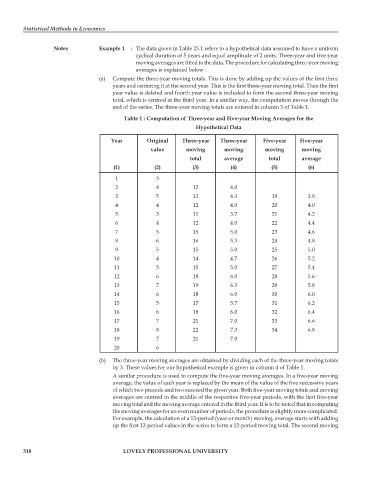
Notes Example 1 : The data given in Table 25.1 refers to a hypothetical data assumed to have a uniform
cyclical duration of 5 years and equal amplitude of 2 units. Three-year and five-year
moving averages are fitted to the data. The procedure for calculating three-year moving
averages is explained below :
(a) Compute the three-year moving totals. This is done by adding up the values of the first three
years and centering it at the second year. This is the first three-year moving total. Then the first
year value is deleted and fourth year value is included to form the second three-year moving
total, which is centred at the third year. In a similar way, the computation moves through the
end of the series. The three-year moving totals are entered in column 3 of Table 1.
Table 1 : Computation of Three-year and Five-year Moving Averages for the
Hypothetical Data
Year Original Three-year Three-year Five-year Five-year
value moving moving moving moving
total average total average
(1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6)
1 3
2 4 12 4.0
3 5 13 4.3 19 3.8
4 4 12 4.0 20 4.0
5 3 11 3.7 21 4.2
6 4 12 4.0 22 4.4
7 5 15 5.0 23 4.6
8 6 16 5.3 24 4.8
9 5 15 5.0 25 5.0
10 4 14 4.7 26 5.2
11 5 15 5.0 27 5.4
12 6 18 6.0 28 5.6
13 7 19 6.3 29 5.8
14 6 18 6.0 30 6.0
15 5 17 5.7 31 6.2
16 6 18 6.0 32 6.4
17 7 21 7.0 33 6.6
18 8 22 7.3 34 6.8
19 7 21 7.0
20 6
(b) The three-year moving averages are obtained by dividing each of the three-year moving totals
by 3. These values for our hypothetical example is given in column 4 of Table 1.
A similar procedure is used to compute the five-year moving averages. In a five-year moving
average, the value of each year is replaced by the mean of the value of the five successive years
of which two precede and two succeed the given year. Both five-year moving totals and moving
averages are centred in the middle of the respective five-year periods, with the first five-year
moving total and the moving average entered in the third year. It is to be noted that in computing
the moving averages for an even number of periods, the procedure is slightly more complicated.
For example, the calculation of a 12-period (year or month) moving, average starts with adding
up the first 12-period values in the series to form a 12-period moving total. The second moving
318 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY