Page 143 - DEDU503_EDUCATIONAL_MANAGEMENT_ENGLISH
P. 143
Unit 11: Leadership Style and Theories of Leadership
11.3.5 Fiedler’s Contingency Theory of Leadership Notes
Fred Fiedler (1967) developed this theory and said that neither situational characteristics nor leader
characteristics alone accounted for group productivity. To him it was a combination of both that
mattered. Leadership effectiveness, according to him, as measured by group performance is an
outcome of the dynamic interplay between leader and situation both. In other words, he meant that
the performance of the leader depended on appropriate matching of leader and situation. Fiedler
pointed out that neither the considerate leader nor the structuring leader is consistently more effective.
Similarly, participative management has been effective in some situations but not in others. On the
other hand, critical factors inherent in the situation in which leadership is exercised determine the
effectiveness of the leadership. He conceptualized these critical factors as the favourableness of the
situation and said that the effectiveness of the leadership depends on the favourableness of the
situation in terms of three characteristics :
(i) Relationship between the leader and the followers
(ii) The degree to which the task is well-structured
(iii) Power of the leader’s position.
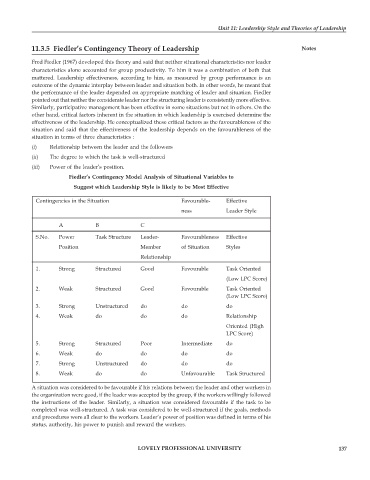
Fiedler’s Contingency Model Analysis of Situational Variables to
Suggest which Leadership Style is likely to be Most Effective
Contingencies in the Situation Favourable- Effective
ness Leader Style
A B C
S.No. Power Task Structure Leader- Favourableness Effective
Position Member of Situation Styles
Relationship
1. Strong Structured Good Favourable Task Oriented
(Low LPC Score)
2. Weak Structured Good Favourable Task Oriented
(Low LPC Score)
3. Strong Unstructured do do do
4. Weak do do do Relationship
Oriented (High
LPC Score)
5. Strong Structured Poor Intermediate do
6. Weak do do do do
7. Strong Unstructured do do do
8. Weak do do Unfavourable Task Structured
A situation was considered to be favourable if his relations between the leader and other workers in
the organization were good, if the leader was accepted by the group, if the workers willingly followed
the instructions of the leader. Similarly, a situation was considered favourable if the task to be
completed was well-structured. A task was considered to be well-structured if the goals, methods
and procedures were all clear to the workers. Leader’s power of position was defined in terms of his
status, authority, his power to punish and reward the workers.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 137