Page 149 - DEDU504_EDUCATIONAL_MEASUREMENT_AND_EVALUATION_ENGLISH
P. 149
Unit 10 : Item Analysis : Item Difficulty, Discrimination index, Effectiveness of Distractors
1.00 Notes
0.90
0.80
0.70
Question Question
Discrimi 0.60 too easy too difficult
-nation 0.50
Index
0.40
0.30
0.20
0.10
0.00
0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0
Difficulty Index
Difficulty Index
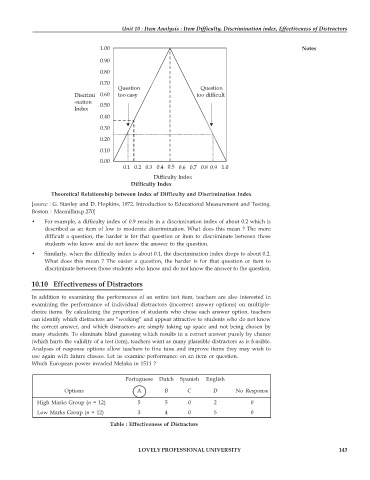
Theoretical Relationship between Index of Difficulty and Discrimination Index
[source : G. Stanley and D. Hopkins, 1972. Introduction to Educational Measurement and Testing.
Boston : Macmillan.p.270]
• For example, a difficulty index of 0.9 results in a discrimination index of about 0.2 which is
described as an item of low to moderate discrimination. What does this mean ? The more
difficult a question, the harder is for that question or item to discriminate between those
students who know and do not know the answer to the question.
• Similarly, when the difficulty index is about 0.1, the discrimination index drops to about 0.2.
What does this mean ? The easier a question, the harder is for that question or item to
discriminate between those students who know and do not know the answer to the question.
10.10 Effectiveness of Distractors
In addition to examining the performance of an entire test item, teachers are also interested in
examining the performance of individual distractors (incorrect answer options) on multiple-
choice items. By calculating the proportion of students who chose each answer option, teachers
can identify which distractors are “working” and appear attractive to students who do not know
the correct answer, and which distractors are simply taking up space and not being chosen by
many students. To eliminate blind guessing which results in a correct answer purely by chance
(which hurts the validity of a test item), teachers want as many plausible distractors as is feasible.
Analyses of response options allow teachers to fine tune and improve items they may wish to
use again with future classes. Let us examine performance on an item or question.
Which European power invaded Melaka in 1511 ?
Portuguese Dutch Spanish English
Options A B C D No Response
High Marks Group (n = 12) 5 5 0 2 0
Low Marks Group (n = 12) 3 4 0 5 0
Table : Effectiveness of Distractors
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 143