Page 230 - DEDU504_EDUCATIONAL_MEASUREMENT_AND_EVALUATION_ENGLISH
P. 230
Educational Measurement and Evaluation
Notes the approach, grading may be Direct grading and Indirect grading. When the reference point is
the standard of judgment, grading may be termed Absolute grading and Relative grading.
Direct Grading
When the performance of students is assessed in qualitative terms and the impression the examiner
or the teacher makes is expressed directly in terms of letter grades, it is Direct grading. This
method of direct grading can be used for assessment of both cognitive and non-cognitive learning
outcomes. However, it is preferred for assessment of non-cognitive outcomes of learning. Non-
cognitive outcomes can be listed stage-wise, assessed and reported separately in terms of letter
grades. Depending on the nature and quality of the attribute assessed, 3-point or 5-point scale
may be used for grading. This direct grading helps minimise inter-examiner variability besides
its easiness to use compared with other methods. However, direct grading lacks diagnostic role,
discourages competition and is devoid of transparency.
Indirect Grading
In this case students’ performance is assessed in terms of marks, which are then transformed into
letter grades, using different methods.
Absolute Grading
It is based on pre-determined standard, which becomes the reference point for assessing students’
performance. This involve direct conversion of marks into grades, categorising students into
different groups like first, second and third divisions as exemplified below.
(i) Distinction : 75% and above
(ii) First division : 60% to 74%
(iii) Second division : 45% to 59%
(iv) Third division : 33% to 44%
(v) Unsatisfactory (fail) : Below 33%
In spite of same range of categories for different subjects, grades may not be comparable because
marks are not comparable and distribution of marks varies from subject to subject and from year
to year in a given subject. Thus a number of students placed in different categories would differ
from subject to subject and year to year, making them uncomparable.
However, in criterion-referenced tests each student is assessed individually in terms of intended
learning outcomes, usually stated in terms of competencies implied in instructional objectives.
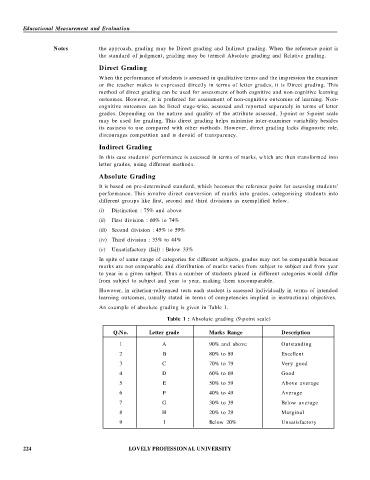
An example of absolute grading is given in Table 1.
Table 1 : Absolute grading (9-point scale)
Q.No. Letter grade Marks Range Description
1 A 90% and above Outstanding
2 B 80% to 89 Excellent
3 C 70% to 79 Very good
4 D 60% to 69 Good
5 E 50% to 59 Above average
6 F 40% to 49 Average
7 G 30% to 39 Below average
8 H 20% to 29 Marginal
9 I Below 20% Unsatisfactory
224 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY