Page 231 - DEDU504_EDUCATIONAL_MEASUREMENT_AND_EVALUATION_ENGLISH
P. 231
Unit 19 : Grading - Need, Problems, Components and Methods
This method involves simple procedure, and the meaning of each grade is understood. Criterion Notes
being the focal point; the student discover their strengths and weaknesses and each student can
strive for attaining the highest grade. One limitation of this method is that scores are taken as
such without considering the errors of measurement that creep in due to various subjective
factors. Another limitation is that the cut-off scores for various categories are decided arbitrarily.
Relative Grading
This type of grading is called grading on the curve, which refers to normal distribution curve. In
this case it is pre-determined what percentage of students are expected to receive the number of
As, Bs, Cs, Ds and so on with reference to a particular group. That is why relative grading is also
called ‘norm-referenced grading’. Steps involved in grading are as follows.
(a) Pupils are expected to acquire new competencies, which become the basis for testing of
sampled behaviour outcomes.
(b) Tests developed provide evidences on students’ learning or achievement, which lead to
award of marks.
(c) These marks when plotted on a graph leading to formation of distribution curve (obtained),
which may be positively or negatively skewed. This obtained curve is converted into normal
curve on the premise that there is a difference between the true level of achievement and
the perceived level of achievement as yielded by tests. True level of achievement is expected
to be normally distributed in a large population irrespective of curricular area.
(d) When perceived curve is transformed into a normal curve, the obtained scores can be
classified into desired number of categories of grades. This is done by using mean of 5 and
standard deviation of 2, and grade value will range from 1 to 9 categories. Two-tail categories
at either end of distribution are combined to make 9 (Stanine scale) in place of 11 categories.
In this way we will have grade-wise distribution of scores (Table 2).
∝
∝ σ σ σ σ σ σ σ σ σ σ σ σ σ σ σ
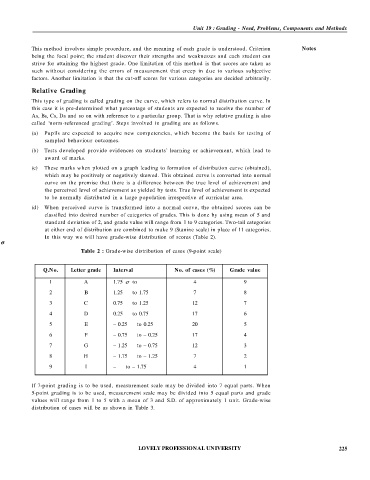
Table 2 : Grade-wise distribution of cases (9-point scale)
Q.No. Letter grade Interval No. of cases (%) Grade value
1 A 1.75 σ to 4 9
2 B 1.25 to 1.75 7 8
3 C 0.75 to 1.25 12 7
4 D 0.25 to 0.75 17 6
5 E – 0.25 to 0.25 20 5
6 F – 0.75 to – 0.25 17 4
7 G – 1.25 to – 0.75 12 3
8 H – 1.75 to – 1.25 7 2
9 I – to – 1.75 4 1
If 7-point grading is to be used, measurement scale may be divided into 7 equal parts. When
5-point grading is to be used, measurement scale may be divided into 5 equal parts and grade
values will range from 1 to 5 with a mean of 3 and S.D. of approximately 1 unit. Grade-wise
distribution of cases will be as shown in Table 3.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 225