Page 80 - DEDU504_EDUCATIONAL_MEASUREMENT_AND_EVALUATION_ENGLISH
P. 80
Educational Measurement and Evaluation
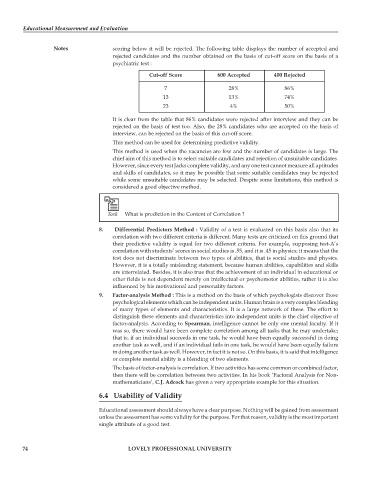
Notes scoring below it will be rejected. The following table displays the number of accepted and
rejected candidates and the number obtained on the basis of cut-off score on the basis of a
psychiatric test :
Cut-off Score 600 Accepted 400 Rejected
7 28% 86%
13 13% 74%
23 4% 50%
It is clear from the table that 86% candidates were rejected after interview and they can be
rejected on the basis of test too. Also, the 28% candidates who are accepted on the basis of
interview, can be rejected on the basis of this cut-off score.
This method can be used for determining predictive validity.
This method is used when the vacancies are few and the number of candidates is large. The
chief aim of this method is to select suitable candidates and rejection of unsuitable candidates.
However, since every test Jacks complete validity, and any one test cannot measure all aptitudes
and skills of candidates, so it may be possible that some suitable candidates may be rejected
while some unsuitable candidates may be selected. Despite some limitations, this method is
considered a good objective method.
What is prediction in the Content of Correlation ?
8. Differential Predictors Method : Validity of a test is evaluated on this basis also that its
correlation with two different criteria is different. Many tests are criticized on this ground that
their predictive validity is equal for two different criteria. For example, supposing test-A’s
correlation with students’ scores in social studies is .55, and it is .45 in physics; it means that the
test does not discriminate between two types of abilities, that is social studies and physics.
However, it is a totally misleading statement, because human abilities, capabilities and skills
are interrelated. Besides, it is also true that the achievement of an individual in educational or
other fields is not dependent merely on intellectual or psychomotor abilities, rather it is also
influenced by his motivational and personality factors.
9. Factor-analysis Method : This is a method on the basis of which psychologists discover those
psychological elements which can be independent units. Human brain is a very complex blending
of many types of elements and characteristics. It is a large network of these. The effort to
distinguish these elements and characteristics into independent units is the chief objective of
factor-analysis. According to Spearman, intelligence cannot be only one mental faculty. If it
was so, there would have been complete correlation among all tasks that he may undertake;
that is, if an individual succeeds in one task, he would have been equally successful in doing
another task as well, and if an individual fails in one task, he would have been equally failure
in doing another task as well. However, in fact it is not so. On this basis, it is said that intelligence
or complete mental ability is a blending of two elements.
The basis of factor-analysis is correlation. If two activities has some common or combined factor,
then there will be correlation between two activities. In his book ‘Factoral Analysis for Non-
mathematicians’, C.J. Adcock has given a very appropriate example for this situation.
6.4 Usability of Validity
Educational assessment should always have a clear purpose. Nothing will be gained from assessment
unless the assessment has some validity for the purpose. For that reason, validity is the most important
single attribute of a good test.
74 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY