Page 65 - DENG504_LINGUISTICS
P. 65
Unit 5: Classification of Speech Sounds: Vowels, Consonants-General Introduction
Notes
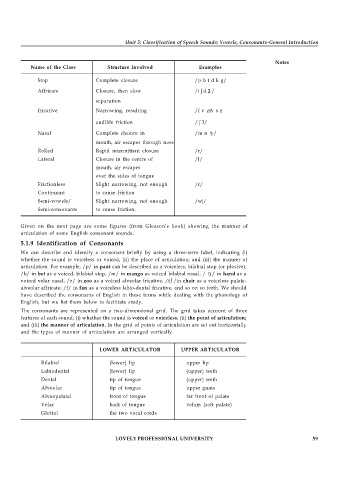
Name of the Class Structure Involved Examples
Stop Complete closure /p b t d k g/
Affricate Closure, then slow /t d /
separation
fricative Narrowing, resulting /f v ð s z
audible friction / 3/
Nasal Complete clsoure in /m n ŋ /
mouth, air escapes through nose
Rolled Rapid intermittent closure /r/
Lateral Closure in the centre of /l/
mouth, air escapes
over the sides of tongue
Frictionless Slight narrowing, not enough /r/
Continuant to cause friction
Semi-vowels/ Slight narrowing, not enough /wj/
Semi-consonants to cause friction.
Given on the next page are some figures (from Gleason’s book) showing the manner of
articulation of some English consonant sounds.
5.1.9 Identification of Consonants
We can describe and identify a consonant briefly by using a three-term label, indicating (i)
whether the sound is voiceless or voiced, (ii) the place of articulation; and (iii) the manner of
articulation. For example, /p/ in pant can be described as a voiceless, bilabial stop (or plosive),
/b/ in bet as a voiced, bilabial stop, /m/ in mango as voiced bilabial nasal, / ŋ / in hand as a
voiced velar nasal, /z/ in zoo as a voiced alveolar fricative, /t /in chair as a voiceless palate-
alveolar affricate; /f/ in fan as a voiceless labio-dental fricative, and so on so forth. We should
have described the consonants of English in these terms while dealing with the phonology of
English, but we list them below to facilitate study:
The consonants are represented on a two-dimensional grid. The grid takes account of three
features of each sound; (i) whether the sound is voiced or voiceless; (ii) the point of articulation;
and (iii) the manner of articulation. In the grid of points of articulation are set out horizontally
and the types of manner of articulation are arranged vertically.
LOWER ARTICULATOR UPPER ARTICULATOR
Bilabial (lower) lip upper lip
Labiodental (lower) lip (upper) teeth
Dental tip of tongue (upper) teeth
Alveolar tip of tongue upper gums
Alveopalatal front of tongue far front of palate
Velar back of tongue velum (soft palate)
Glottal the two vocal cords
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 59