Page 132 - DMTH404_STATISTICS
P. 132
Statistics
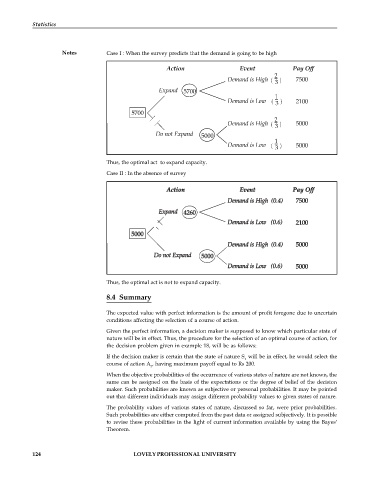
Notes Case I : When the survey predicts that the demand is going to be high
Thus, the optimal act to expand capacity.
Case II : In the absence of survey
Action Event Pay Off
Demand is High (0.4) 7500
Expand 4260
Demand is Low (0.6) 2100
5000
Demand is High (0.4) 5000
Do not Expand 5000
Demand is Low (0.6) 5000
Thus, the optimal act is not to expand capacity.
8.4 Summary
The expected value with perfect information is the amount of profit foregone due to uncertain
conditions affecting the selection of a course of action.
Given the perfect information, a decision maker is supposed to know which particular state of
nature will be in effect. Thus, the procedure for the selection of an optimal course of action, for
the decision problem given in example 18, will be as follows:
If the decision maker is certain that the state of nature S will be in effect, he would select the
1
course of action A , having maximum payoff equal to Rs 200.
3
When the objective probabilities of the occurrence of various states of nature are not known, the
same can be assigned on the basis of the expectations or the degree of belief of the decision
maker. Such probabilities are known as subjective or personal probabilities. It may be pointed
out that different individuals may assign different probability values to given states of nature.
The probability values of various states of nature, discussed so far, were prior probabilities.
Such probabilities are either computed from the past data or assigned subjectively. It is possible
to revise these probabilities in the light of current information available by using the Bayes'
Theorem.
124 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY