Page 50 - DCOM101_FINANCIAL_ACCOUNTING_I
P. 50
Financial Accounting-I
Notes fi les) which provide the fi rst indication that a transaction has taken place (or will be taking
place in the future.)
2. Preparing Journals: The journal is the “book of original entry,” the place where the
transactions first become part of the offi cial financial records of the organization. We make
journal entries which specify the accounts which are affected by a transaction, and the
amount of money involved.
3. Post to Ledger A/c: The ledger is the entire group of accounts maintained by an organization.
Posting refers to the transfer of the journal entries to the ledger. In a manual system,
posting was a separate process. In computerized systems, posting is typically accomplished
contemporaneously with recording the transaction in the journal.
4. Preparation of Trial Balance: A trial balance is nothing more than a summation of the
account balances to be sure that the books do, in fact, balance.
5. Prepare fi nancial statements: After preparing the trial balance the next step is to prepare
the financial statements like income statement, balance sheet and cash fl ow statement.
6. Post Closing Entries: Closing entries are the entries that we make to close the temporary
accounts (the expense and revenue accounts). In manual systems, each closing entry had to
be made individually. In computerized systems, a single command closes the books.
7. Preparation of Financial Statement: Last step includes the preparation of Trading and
Profit & Loss A/c and opening and closing balance sheet.
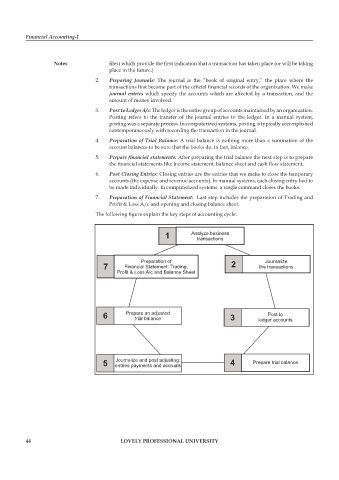
The following figure explain the key steps of accounting cycle:
1 Analyze business
transactions
Preparation of Journalize
7 Financial Statement: Trading, 2 the transactions
Profit & Loss A/c and Balance Sheet
6 Prepare an adjusted 3 ledger accounts
Post to
trial balance
Journalize and post adjusting:
5 entries payments and accruals 4 Prepare trial balance
44 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY