Page 28 - DCOM203_DMGT204_QUANTITATIVE_TECHNIQUES_I
P. 28
Unit 2: Classification of Data
Notes
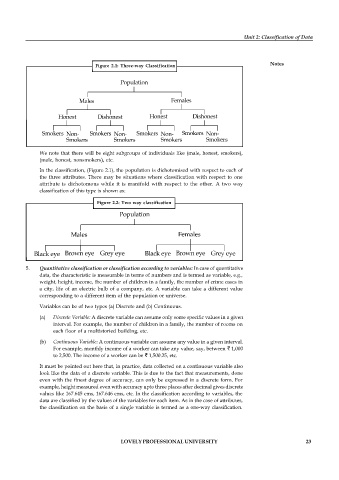
Figure 2.1: Three-way Classification
We note that there will be eight subgroups of individuals like (male, honest, smokers),
(male, honest, nonsmokers), etc.
In the classification, (Figure 2.1), the population is dichotomised with respect to each of
the three attributes. There may be situations where classification with respect to one
attribute is dichotomous while it is manifold with respect to the other. A two way
classification of this type is shown as:
Figure 2.2: Two way classification
5. Quantitative classification or classification according to variables: In case of quantitative
data, the characteristic is measurable in terms of numbers and is termed as variable, e.g.,
weight, height, income, the number of children in a family, the number of crime cases in
a city, life of an electric bulb of a company, etc. A variable can take a different value
corresponding to a different item of the population or universe.
Variables can be of two types (a) Discrete and (b) Continuous.
(a) Discrete Variable: A discrete variable can assume only some specific values in a given
interval. For example, the number of children in a family, the number of rooms on
each floor of a multistoried building, etc.
(b) Continuous Variable: A continuous variable can assume any value in a given interval.
For example, monthly income of a worker can take any value, say, between 1,000
to 2,500. The income of a worker can be 1,500.25, etc.
It must be pointed out here that, in practice, data collected on a continuous variable also
look like the data of a discrete variable. This is due to the fact that measurements, done
even with the finest degree of accuracy, can only be expressed in a discrete form. For
example, height measured even with accuracy upto three places after decimal gives discrete
values like 167.645 cms, 167.646 cms, etc. In the classification according to variables, the
data are classified by the values of the variables for each item. As in the case of attributes,
the classification on the basis of a single variable is termed as a one-way classification.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 23