Page 30 - DCOM203_DMGT204_QUANTITATIVE_TECHNIQUES_I
P. 30
Unit 2: Classification of Data
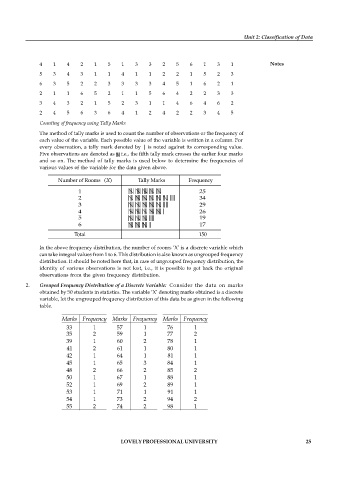
4 1 4 2 1 5 1 3 3 2 5 6 1 3 1 Notes
5 3 4 3 1 1 4 1 1 2 2 1 5 2 3
6 3 5 2 2 3 3 3 3 4 5 1 6 2 1
2 1 1 6 5 2 1 1 5 6 4 2 2 3 3
3 4 3 2 1 5 2 3 1 1 4 6 4 6 2
2 4 5 6 3 6 4 1 2 4 2 2 3 4 5
Counting of frequency using Tally Marks
The method of tally marks is used to count the number of observations or the frequency of
each value of the variable. Each possible value of the variable is written in a column. For
every observation, a tally mark denoted by | is noted against its corresponding value.
Five observations are denoted as i.e., the fifth tally mark crosses the earlier four marks
and so on. The method of tally marks is used below to determine the frequencies of
various values of the variable for the data given above.
In the above frequency distribution, the number of rooms ‘X’ is a discrete variable which
can take integral values from 1 to 6. This distribution is also known as ungrouped frequency
distribution. It should be noted here that, in case of ungrouped frequency distribution, the
identity of various observations is not lost, i.e., it is possible to get back the original
observations from the given frequency distribution.
2. Grouped Frequency Distribution of a Discrete Variable: Consider the data on marks
obtained by 50 students in statistics. The variable ‘X’ denoting marks obtained is a discrete
variable, let the ungrouped frequency distribution of this data be as given in the following
table.
33 1 57 1 76 1
35 2 59 1 77 2
39 1 60 2 78 1
41 2 61 1 80 1
42 1 64 1 81 1
45 1 65 3 84 1
48 2 66 2 85 2
50 1 67 1 88 1
52 1 69 2 89 1
53 1 71 1 91 1
54 1 73 2 94 2
55 2 74 2 98 1
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 25