Page 307 - DCOM203_DMGT204_QUANTITATIVE_TECHNIQUES_I
P. 307
Quantitative Techniques – I
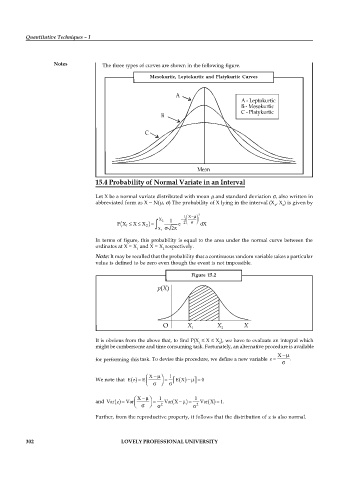
Notes The three types of curves are shown in the following figure.
Mesokurtic, Leptokurtic and Platykurtic Curves
15.4 Probability of Normal Variate in an Interval
Let X be a normal variate distributed with mean and standard deviation , also written in
abbreviated form as X ~ N( , ) The probability of X lying in the interval (X , X ) is given by
1 2
2
1 X
X 2 1
P X X X e 2 dX
1 2
X 1 2
In terms of figure, this probability is equal to the area under the normal curve between the
ordinates at X = X and X = X respectively.
1 2
Note: It may be recalled that the probability that a continuous random variable takes a particular
value is defined to be zero even though the event is not impossible.
Figure 15.2
It is obvious from the above that, to find P(X X X ), we have to evaluate an integral which
1 2
might be cumbersome and time consuming task. Fortunately, an alternative procedure is available
X
for performing this task. To devise this procedure, we define a new variable z .
X 1
We note that E z E E X 0
X 1 1
and Var z Var 2 Var X 2 Var X 1.
Further, from the reproductive property, it follows that the distribution of z is also normal.
302 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY