Page 105 - DCOM206_COST_ACCOUNTING_II
P. 105
Cost Accounting – II
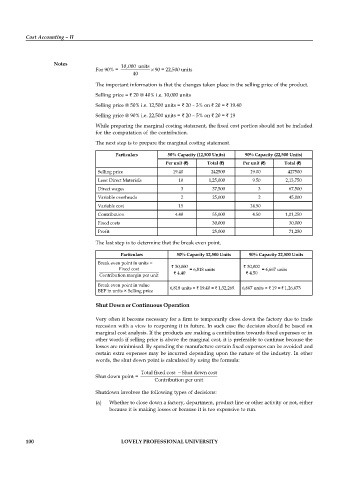
Notes 10,000 units
For 90% = 90 = 22,500 units
40
The important information is that the changes taken place in the selling price of the product.
Selling price = ` 20 @ 40% i.e. 10,000 units
Selling price @ 50% i.e. 12,500 units = ` 20 – 3% on ` 20 = ` 19.40
Selling price @ 90% i.e. 22,500 units = ` 20 – 5% on ` 20 = ` 19
While preparing the marginal costing statement, the fixed cost portion should not be included
for the computation of the contribution.
The next step is to prepare the marginal costing statement.
Particulars 50% Capacity (12,500 Units) 90% Capacity (22,500 Units)
Per unit (`) Total (`) Per unit (`) Total (`)
Selling price 19.40 242500 19.00 427500
Less: Direct Materials 10 1,25,000 9.50 2,13,750
Direct wages 3 37,500 3 67,500
Variable overheads 2 25,000 2 45,000
Variable cost 15 14.50
Contribution 4.40 55,000 4.50 1,01,250
Fixed costs 30,000 30,000
Profit 25,000 71,250
The last step is to determine that the break even point.
Particulars 50% Capacity 12,500 Units 90% Capacity 22,500 Units
Break even point in units =
` 30,000 ` 30,000
Fixed cost = 6,818 units = 6,667 units
` 4.40 ` 4.50
Contribution margin per unit
Break even point in value 6,818 units × ` 19.40 = ` 1,32,269. 6,667 units × ` 19 = ` 1,26,673
BEP in units × Selling price
Shut Down or Continuous Operation
Very often it become necessary for a firm to temporarily close down the factory due to trade
recession with a view to reopening it in future. In such case the decision should be based on
marginal cost analysis. If the products are making a contribution towards fixed expenses or in
other words if selling price is above the marginal cost, it is preferable to continue because the
losses are minimised. By spending the manufacture certain fixed expenses can be avoided and
certain extra expenses may be incurred depending upon the nature of the industry. In other
words, the shut down point is calculated by using the formula:
Total fixed cost Shut down cost
Shut down point =
Contribution per unit
Shutdown involves the following types of decisions:
(a) Whether to close down a factory, department, product line or other activity or not, either
because it is making losses or because it is too expensive to run.
100 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY