Page 172 - DMGT209_QUANTITATIVE_TECHNIQUES_II
P. 172
Unit 9: Attitude Measurement and Scaling Techniques
Notes
Example: Sales this year for product A are twice the sales of the same product last year.
Statistical implications: All statistical operations can be performed on this scale.
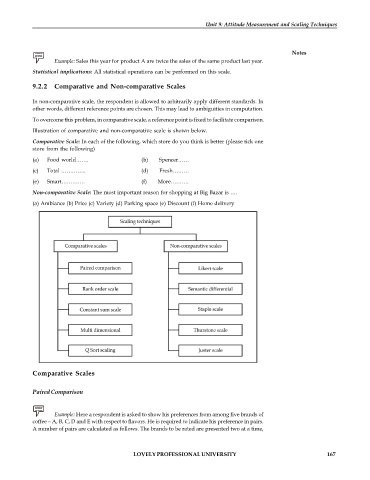
9.2.2 Comparative and Non-comparative Scales
In non-comparative scale, the respondent is allowed to arbitrarily apply different standards. In
other words, different reference points are chosen. This may lead to ambiguities in computation.
To overcome this problem, in comparative scale, a reference point is fixed to facilitate comparison.
Illustration of comparative and non-comparative scale is shown below.
Comparative Scale: In each of the following, which store do you think is better (please tick one
store from the following)
(a) Food world……. (b) Spencer……
(c) Total ………….. (d) Fresh………
(e) Smart…………. (f) More……….
Non-comparative Scale: The most important reason for shopping at Big Bazar is ….
(a) Ambiance (b) Price (c) Variety (d) Parking space (e) Discount (f) Home delivery
Comparative Scales
Paired Comparison
Example: Here a respondent is asked to show his preferences from among five brands of
coffee – A, B, C, D and E with respect to flavors. He is required to indicate his preference in pairs.
A number of pairs are calculated as follows. The brands to be rated are presented two at a time,
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 167