Page 183 - DMGT209_QUANTITATIVE_TECHNIQUES_II
P. 183
Quantitative Techniques-II
Notes 5. Semantic Differential Scale is very similar to the ....................... Scale.
6. The Likert Scale consists of two parts – .................... and ..........................
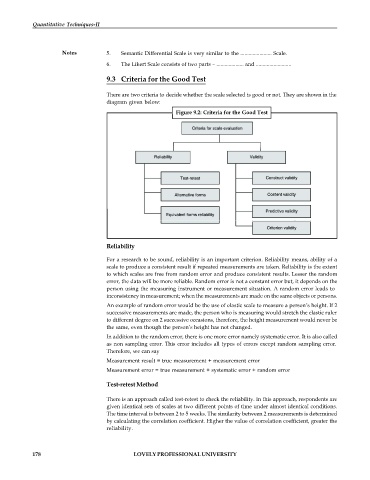
9.3 Criteria for the Good Test
There are two criteria to decide whether the scale selected is good or not. They are shown in the
diagram given below:
Figure 9.2: Criteria for the Good Test
Reliability
For a research to be sound, reliability is an important criterion. Reliability means, ability of a
scale to produce a consistent result if repeated measurements are taken. Reliability is the extent
to which scales are free from random error and produce consistent results. Lesser the random
error, the data will be more reliable. Random error is not a constant error but, it depends on the
person using the measuring instrument or measurement situation. A random error leads to
inconsistency in measurement; when the measurements are made on the same objects or persons.
An example of random error would be the use of elastic scale to measure a person’s height. If 2
successive measurements are made, the person who is measuring would stretch the elastic ruler
to different degree on 2 successive occasions, therefore, the height measurement would never be
the same, even though the person’s height has not changed.
In addition to the random error, there is one more error namely systematic error. It is also called
as non sampling error. This error includes all types of errors except random sampling error.
Therefore, we can say
Measurement result = true measurement + measurement error
Measurement error = true measurement + systematic error + random error
Test-retest Method
There is an approach called test-retest to check the reliability. In this approach, respondents are
given identical sets of scales at two different points of time under almost identical conditions.
The time interval is between 2 to 5 weeks. The similarity between 2 measurements is determined
by calculating the correlation coefficient. Higher the value of correlation coefficient, greater the
reliability.
178 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY