Page 109 - DCOM302_MANAGEMENT_ACCOUNTING
P. 109
Management Accounting
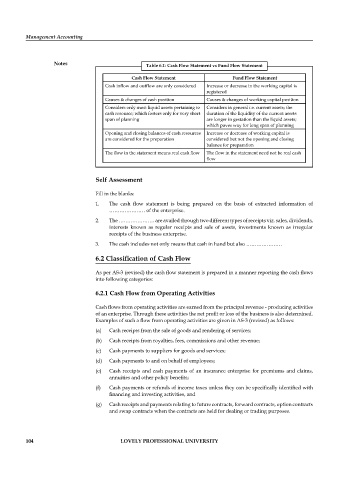
Notes Table 6.1: Cash Flow Statement vs Fund Flow Statement
Cash Flow Statement Fund Flow Statement
Cash inflow and outflow are only considered Increase or decrease in the working capital is
registered
Causes & changes of cash position Causes & changes of working capital position
Considers only most liquid assets pertaining to Considers in general i.e. current assets; the
cash resource; which fosters only for very short duration of the liquidity of the current assets
span of planning are longer in gestation than the liquid assets;
which paves way for long span of planning
Opening and closing balances of cash resources Increase or decrease of working capital is
are considered for the preparation considered but not the opening and closing
balance for preparation
The flow in the statement means real cash fl ow The flow in the statement need not be real cash
fl ow
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
1. The cash flow statement is being prepared on the basis of extracted information of
………………… of the enterprise.
2. The ………………… are availed through two different types of receipts viz. sales, dividends,
interests known as regular receipts and sale of assets, investments known as irregular
receipts of the business enterprise.
3. The cash includes not only means that cash in hand but also …………………
6.2 Classification of Cash Flow
As per AS-3 (revised) the cash flow statement is prepared in a manner reporting the cash fl ows
into following categories:
6.2.1 Cash Flow from Operating Activities
Cash flows from operating activities are earned from the principal revenue - producing activities
of an enterprise. Through these activities the net profit or loss of the business is also determined.
Examples of such a flow from operating activities are given in AS-3 (revised) as follows:
(a) Cash receipts from the sale of goods and rendering of services;
(b) Cash receipts from royalties, fees, commissions and other revenue;
(c) Cash payments to suppliers for goods and services;
(d) Cash payments to and on behalf of employees;
(e) Cash receipts and cash payments of an insurance enterprise for premiums and claims,
annuities and other policy benefi ts;
(f) Cash payments or refunds of income taxes unless they can be specifi cally identifi ed with
financing and investing activities, and
(g) Cash receipts and payments relating to future contracts, forward contracts, option contracts
and swap contracts when the contracts are held for dealing or trading purposes.
104 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY