Page 22 - DCOM302_MANAGEMENT_ACCOUNTING
P. 22
Unit 2: Understanding Corporate Financial Statements
The receipts which arise out of normal course of a business are known as Revenue Receipts. Notes
For example, income from sale of goods.
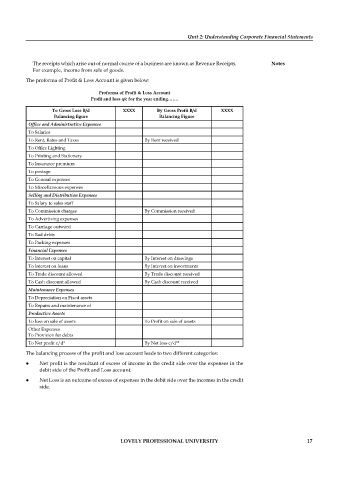
The proforma of Profit & Loss Account is given below:
Proforma of Profit & Loss Account
Profit and loss a/c for the year ending…….
To Gross Loss B/d XXXX By Gross Profi t B/d XXXX
Balancing fi gure Balancing Figure
Office and Administrative Expenses
To Salaries
To Rent, Rates and Taxes By Rent received
To Offi ce Lighting
To Printing and Stationery
To Insurance premium
To postage
To General expenses
To Miscellaneous expenses
Selling and Distribution Expenses
To Salary to sales staff
To Commission charges By Commission received
To Advertising expenses
To Carriage outward
To Bad debts
To Packing expenses
Financial Expenses
To Interest on capital By Interest on drawings
To Interest on loans By Interest on investments
To Trade discount allowed By Trade discount received
To Cash discount allowed By Cash discount received
Maintenance Expenses
To Depreciation on Fixed assets
To Repairs and maintenance of
Productive Assets
To loss on sale of assets To Profit on sale of assets
Other Expenses
To Provision for debts
To Net profit c/d* By Net loss c/d**
The balancing process of the profit and loss account leads to two different categories:
Net profit is the resultant of excess of income in the credit side over the expenses in the
debit side of the Profit and Loss account.
Net Loss is an outcome of excess of expenses in the debit side over the incomes in the credit
side.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 17