Page 40 - DCOM302_MANAGEMENT_ACCOUNTING
P. 40
Unit 3: Analysis of Financial Statements
13. Computation of ratios for an accounting period is a form of horizontal analysis. Notes
14. Generally, the last concern of a financial analyst is a firm’s liquidity.
3.5 Trend Analysis
The next important tool of analysis is trend percentage which plays significant role in analyzing
the financial stature of the enterprise through base years’ performance ratio computation. This
not only reveals the trend movement of the financial performance of the enterprise but also
highlights the strengths and weaknesses of the enterprise.
The following ratio is being used to compute the trend percentage
Current year
= ¥ 100
Base year
This trend ratio is being computed for every component for many numbers of years which not
only facilitates comparison but also guides the firm to understand the trend path of the firm.
In the analysis of financial information, trend analysis is the presentation of amounts as a
percentage of a base year.
Example: If I want to see the trend of a company’s revenues, net income, and number of
clients during the years 2001 through 2007, trend analysis will present 2001 as the base year and
the 2001 amounts will be restated to be 100. The amounts for the years 2002 through 2007 will be
presented as the percentages of the 2001 amounts.
In other words, each year’s amounts will be divided by the 2001 amounts and the resulting
percentage will be presented. If revenues for the years 2001 through 2007 might have been `
31,691,000; ` 40,930,000; ` 50,704,00; ` 63,891,000; ` 79,341,000; ` 101,154,000; ` 120,200,000. These
revenue amounts will be restated to be 100, 129, 160, 202, 250, 319, and 379.
From this trend analysis we can see that revenues in 2007 were 379% of the 2001 revenues, net
income in 2007 was 467% of the 2001 net income, and the number of clients in 2007 was 317% of
the number in 2001.
Let’s assume that the net income amounts divided by the 2001 amount ended up as 100, 147, 206,
253, 343, 467, and 423. The number of clients when divided by the base year amount are 100, 122,
149, 184, 229, 277, and 317.
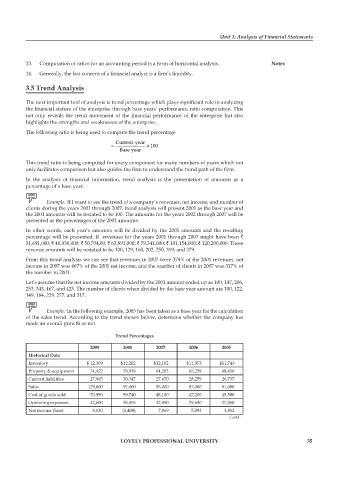
Example: In the following example, 2005 has been taken as a base year for the calculation
of the sales trend. According to the trend shown below, determine whether the company has
made an overall growth or not.
Trend Percentages
2009 2008 2007 2006 2005
Historical Data
Inventory $ 12,309 $12,202 $12,102 $11,973 $11,743
Property & equipment 74,422 78,938 64,203 65,239 68,450
Current liabilities 27,945 30,347 27,670 28,259 26,737
Sales 129,000 97,000 95,000 87,000 81,000
Cost of goods sold 70,950 59,740 48,100 47,200 45,500
Operating expenses 42,600 38,055 32,990 29,690 27,050
Net income (loss) 8,130 (1,400) 7,869 5,093 3,812
Contd…
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 35