Page 238 - DCOM303_DMGT504_OPERATION_RESEARCH
P. 238
Unit 12: Critical Path Method and PERT
Project management generally consists of three phases: Notes
1. Planning: Planning involves setting the objectives of the project. Identifying various
activities to be performed and determining the requirement of resources such as men,
materials, machines, etc. The cost and time for all the activities are estimated, and a
network diagram is developed showing sequential interrelationships (predecessor and
successor) between various activities during the planning stage.
2. Scheduling: Based on the time estimates, the start and finish times for each activity are
worked out by applying forward and backward pass techniques, critical path is identified,
along with the slack and float for the non-critical paths.
3. Controlling: Controlling refers to analyzing and evaluating the actual progress against
the plan. Reallocation of resources, crashing and review of projects with periodical reports
are carried out.
12.1 CPM/PERT Network Components
CPM/PERT networks contains two major components
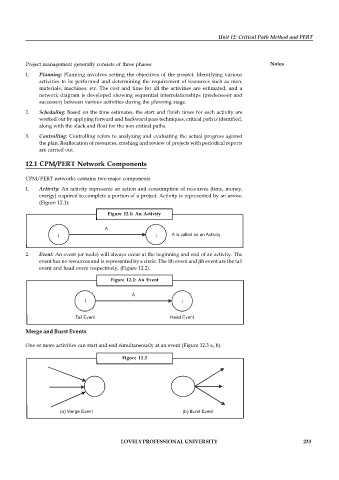
1. Activity: An activity represents an action and consumption of resources (time, money,
energy) required to complete a portion of a project. Activity is represented by an arrow,
(Figure 12.1):
Figure 12.1: An Activity
A
i j A is called as an Activity
2. Event: An event (or node) will always occur at the beginning and end of an activity. The
event has no resources and is represented by a circle. The ith event and jth event are the tail
event and head event respectively, (Figure 12.2).
Figure 12.2: An Event
A
i j
Tail Event Head Event
Merge and Burst Events
One or more activities can start and end simultaneously at an event (Figure 12.3 a, b).
Figure 12.3
(a) Merge Event (b) Burst Event
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 233