Page 28 - DCOM303_DMGT504_OPERATION_RESEARCH
P. 28
Unit 2: Linear Programming Problems
Hence, the objective function is given by, Notes
Maximize ‘Z’ = 10x + 12x + 15x (Subject to constraints)
1 2 3
0.10x + 0.12x + 0.15x 36
1 2 3
0.12x + 0.05x + 0.09x 30 (Production hours constraints)
1 2 3
0.18x + 0 + 0.07x 37
1 3
0.13x + 0.10x + 0.08x 38
1 2 3
x 200
1
x 100 (Sales constraints)
2
x 180
3
x 20 (Production constraints)
1
x 70
2
OR
20 x 200
1
70 x 180 (Sales and Production constraints)
3
x 100
2
x , x , x 0 (Non-negativity constraints)
1 2 3
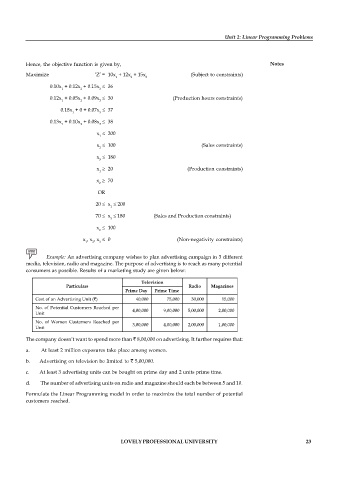
Example: An advertising company wishes to plan advertising campaign in 3 different
media, television, radio and magazine. The purpose of advertising is to reach as many potential
consumers as possible. Results of a marketing study are given below:
Television
Particulars Radio Magazines
Prime Day Prime Time
Cost of an Advertising Unit (`) 40,000 75,000 30,000 15,000
No. of Potential Customers Reached per 4,00,000 9,00,000 5,00,000 2,00,000
Unit
No. of Women Customers Reached per 3,00,000 4,00,000 2,00,000 1,00,000
Unit
The company doesn’t want to spend more than ` 8,00,000 on advertising. It further requires that:
a. At least 2 million exposures take place among women.
b. Advertising on television be limited to ` 5,00,000.
c. At least 3 advertising units can be bought on prime day and 2 units prime time.
d. The number of advertising units on radio and magazine should each be between 5 and 10.
Formulate the Linear Programming model in order to maximize the total number of potential
customers reached.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 23