Page 23 - DCOM304_INDIAN_FINANCIAL_SYSTEM
P. 23
Indian Financial System
Notes Table 2.1, exhibiting data regarding amount of issues during the First Plan to the Seventh Plan
period, shows that yearly average of the amount of new security floated in the market ranged
between ` 17 crore and ` 83 crore during first plan period to fifth plan period. Phenomenal
progress was, however, recorded during Sixth and Seventh plan periods which witnessed surge
in yearly average volume of new issue business to ` 218 crore and ` 559 crore, respectively. The
reasons attributable to this trend were establishment of considerably large number of new
enterprises and expansion and modernization of a large number of existing undertakings leading
to phenomenal spurt in demand for capital, increasing facilities in respect of underwriting of
new capital issues and marketing of securities, participation of national and state level financial
institutions in new issue activity and above all existence of favorable investment climate in the
country. The liberalization of industrial and new capital issue policies in 1984-95 and relaxation
of norms relating to foreign investments and incentives given by the government had given
fillip to sustain the growth in the market.
2.1.2 Security-wise New Issue Activity
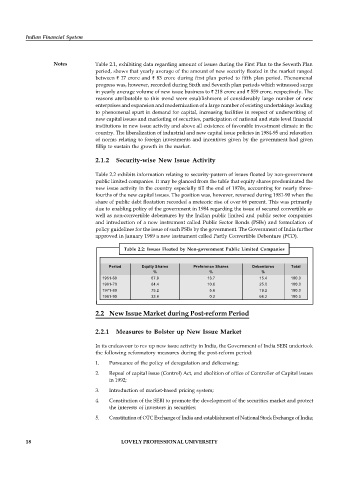
Table 2.2 exhibits information relating to security-pattern of issues floated by non-government
public limited companies. It may be glanced from the table that equity shares predominated the
new issue activity in the country especially till the end of 1970s, accounting for nearly three-
fourths of the new capital issues. The position was, however, reversed during 1981-90 when the
share of public debt floatation recorded a meteoric rise of over 66 percent. This was primarily
due to enabling policy of the government in 1984 regarding the issue of secured convertible as
well as non-convertible debentures by the Indian public limited and public sector companies
and introduction of a new instrument called Public Sector Bonds (PSBs) and formulation of
policy guidelines for the issue of such PSBs by the government. The Government of India further
approved in January 1989 a new instrument called Partly Convertible Debenture (PCD).
Table 2.2: Issues Floated by Non-government Public Limited Companies
Period Equity Shares Preference Shares Debentures Total
% % %
1951-60 67.9 13.7 15.4 100.0
1961-70 64.4 10.6 25.0 100.0
1971-80 75.2 5.6 19.2 100.0
1981-90 33.6 0.2 66.2 100.0
2.2 New Issue Market during Post-reform Period
2.2.1 Measures to Bolster up New Issue Market
In its endeavour to rev up new issue activity in India, the Government of India SEBI undertook
the following reformatory measures during the post-reform period:
1. Pursuance of the policy of deregulation and delicensing;
2. Repeal of capital issue (Control) Act, and abolition of office of Controller of Capital issues
in 1992;
3. Introduction of market-based pricing system;
4. Constitution of the SEBI to promote the development of the securities market and protect
the interests of investors in securities;
5. Constitution of OTC Exchange of India and establishment of National Stock Exchange of India;
18 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY