Page 26 - DCOM304_INDIAN_FINANCIAL_SYSTEM
P. 26
Unit 2: Financial Market Reforms
Increased savings rate among individuals as well as big corpuses of funds available with Notes
insurance companies and mutual funds, and increase in the appetite of FIIs as well as retail
investors also helped in stoking up demand for new issues.
2.3.2 Qualitative Dimension
Not only has there been quantum jump in new issue floatations, there has also been qualitative
change in new issue activity, as manifest from the following discussions:
Security Pattern of New Issues
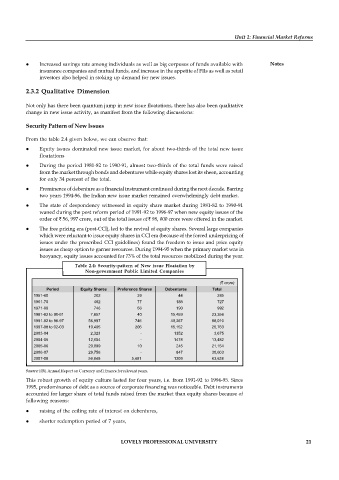
From the table 2.4 given below, we can observe that:
Equity issues dominated new issue market, for about two-thirds of the total new issue
floatations
During the period 1981-82 to 1990-91, almost two-thirds of the total funds were raised
from the market through bonds and debentures while equity shares lost its sheen, accounting
for only 34 percent of the total.
Prominence of debenture as a financial instrument continued during the next decade. Barring
two years 1994-96, the Indian new issue market remained overwhelmingly debt market.
The state of despondency witnessed in equity share market during 1981-82 to 1990-91
waned during the post reform period of 1991-92 to 1996-97 when new equity issues of the
order of ` 56, 997 crore, out of the total issues of ` 98, 000 crore were offered in the market.
The free pricing era (post-CCI), led to the revival of equity shares. Several large companies
which were reluctant to issue equity shares in CCI era (because of the forced underpricing of
issues under the prescribed CCI guidelines) found the freedom to issue and price equity
issues as cheap option to garner resources. During 1994-95 when the primary market was in
buoyancy, equity issues accounted for 73% of the total resources mobilized during the year.
Table 2.4: Security-pattern of New issue Floatation by
Non-government Public Limited Companies
( crore)
`
Period Equity Shares Preference Shares Debentures Total
1951-60 202 39 44 285
1961-70 462 77 188 727
1971-80 746 56 190 992
1981-82 to 90-91 7,857 40 15,459 23,356
1991-92 to 96-97 56,997 746 40,267 98,010
1997-98 to 02-03 10,405 206 15,152 25,763
2003-04 2,323 - 1352 3,675
2004-05 12,004 - 1478 13,482
2005-06 20,899 10 245 21,154
2006-07 29,756 - 847 30,603
2007-08 56,848 5,481 1309 63,638
Source: RBI, Annual Report on Currency and Finance for relevant years.
This robust growth of equity culture lasted for four years, i.e. from 1991-92 to 1994-95. Since
1995, predominance of debt as a source of corporate financing was noticeable. Debt instruments
accounted for larger share of total funds raised from the market than equity shares because of
following reasons:
raising of the ceiling rate of interest on debentures,
shorter redemption period of 7 years,
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 21