Page 61 - DCOM309_INSURANCE_LAWS_AND_PRACTICES
P. 61
Insurance Laws and Practices
Notes
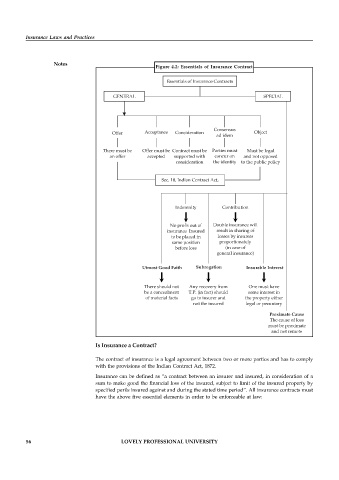
Figure 4.2: Essentials of Insurance Contract
Essentials of Insurance Contracts
GENERAL SPECIAL
Offer Acceptance Consideration Consensus Object
ad idem
There must be Offer must be Contract must be Parties must Must be legal
an offer accepted supported with concur on and not opposed
consideration the identity to the public policy
Sec. 10, Indian Contract Act,
Indemnity Contribution
No profit out of Double insurance will
insurance Insured result in sharing of
to be placed in losses by insurers
same position proportionately
before loss (in case of
general insurance)
Utmost Good Faith Subrogation Insurable Interest
There should not Any recovery from One must have
be a concealment T.P. (in fact) should some interest in
of material facts go to insurer and the property either
not the insured legal or pecuniary
Proximate Cause
The cause of loss
must be proximate
and not remote
Is Insurance a Contract?
The contract of insurance is a legal agreement between two or more parties and has to comply
with the provisions of the Indian Contract Act, 1872.
Insurance can be defined as “a contract between an insurer and insured, in consideration of a
sum to make good the financial loss of the insured, subject to limit of the insured property by
specified perils insured against and during the stated time period”. All insurance contracts must
have the above five essential elements in order to be enforceable at law:
56 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY