Page 103 - DECO405_MANAGERIAL_ECONOMICS
P. 103
Managerial Economics
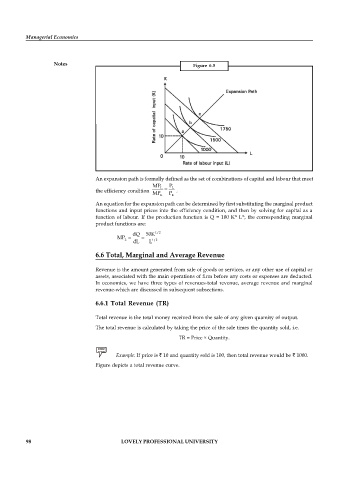
Notes Figure 6.5
An expansion path is formally defined as the set of combinations of capital and labour that meet
MP L P L
the efficiency condition .
MP P
K K
An equation for the expansion path can be determined by first substituting the marginal product
functions and input prices into the efficiency condition, and then by solving for capital as a
½
½
function of labour. If the production function is Q = 100 K L , the corresponding marginal
product functions are:
dQ 50K 1/2
MP
L 1/2
dL L
6.6 Total, Marginal and Average Revenue
Revenue is the amount generated from sale of goods or services, or any other use of capital or
assets, associated with the main operations of firm before any costs or expenses are deducted.
In economics, we have three types of revenues-total revenue, average revenue and marginal
revenue-which are discussed in subsequent subsections.
6.6.1 Total Revenue (TR)
Total revenue is the total money received from the sale of any given quantity of output.
The total revenue is calculated by taking the price of the sale times the quantity sold, i.e.
TR = Price × Quantity.
Example: If price is 10 and quantity sold is 100, then total revenue would be 1000.
Figure depicts a total revenue curve.
98 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY