Page 99 - DECO405_MANAGERIAL_ECONOMICS
P. 99
Managerial Economics
Notes For movements along an isoquant, the level of output remains constant and the ratio of capital
to labour changes continuously. However, a movement from the isoquant to another means
that the level of output changes.
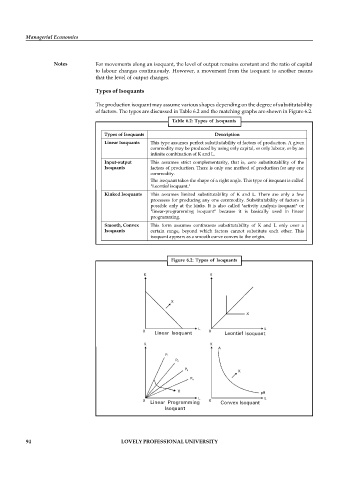
Types of Isoquants
The production isoquant may assume various shapes depending on the degree of substitutability
of factors. The types are discussed in Table 6.2 and the matching graphs are shown in Figure 6.2.
Table 6.2: Types of Isoquants
Types of Isoquants Description
Linear Isoquants This type assumes perfect substitutability of factors of production. A given
commodity may be produced by using only capital, or only labour, or by an
infinite combination of K and L.
Input-output This assumes strict complementarity, that is, zero substitutability of the
Isoquants factors of production. There is only one method of production for any one
commodity.
The isoquant takes the shape of a right angle. This type of isoquant is called
"Leontief isoquant."
Kinked Isoquants This assumes limited substitutability of K and L. There are only a few
processes for producing any one commodity. Substitutability of factors is
possible only at the kinks. It is also called "activity analysis isoquant" or
"linear-programming isoquant" because it is basically used in linear
programming.
Smooth, Convex This form assumes continuous substitutability of K and L only over a
Isoquants certain range, beyond which factors cannot substitute each other. This
isoquant appears as a smooth curve convex to the origin.
Figure 6.2: Types of Isoquants
94 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY