Page 153 - DECO405_MANAGERIAL_ECONOMICS
P. 153
Managerial Economics
Notes 9.2.3 Shut-down Decision
The supply curve of a competitive firm is its marginal curve. It is that part of the marginal cost
curve which is above the average variable cost curve.
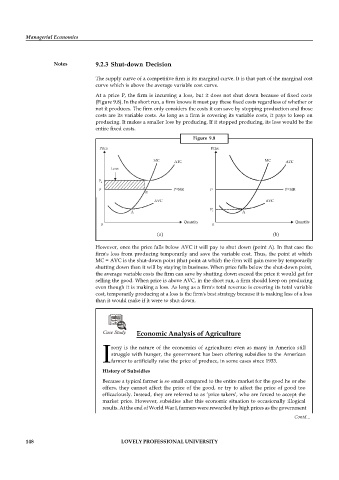
At a price P, the firm is incurring a loss, but it does not shut down because of fixed costs
(Figure 9.8). In the short run, a firm knows it must pay these fixed costs regardless of whether or
not it produces. The firm only considers the costs it can save by stopping production and those
costs are its variable costs. As long as a firm is covering its variable costs, it pays to keep on
producing. It makes a smaller loss by producing. If it stopped producing, its loss would be the
entire fixed costs.
Figure 9.8
(a) (b)
However, once the price falls below AVC it will pay to shut down (point A). In that case the
firm's loss from producing temporarily and save the variable cost. Thus, the point at which
MC = AVC is the shut-down point (that point at which the firm will gain more by temporarily
shutting down than it will by staying in business. When price falls below the shut-down point,
the average variable costs the firm can save by shutting down exceed the price it would get for
selling the good. When price is above AVC, in the short run, a firm should keep on producing
even though it is making a loss. As long as a firm's total revenue is covering its total variable
cost, temporarily producing at a loss is the firm's best strategy because it is making less of a loss
than it would make if it were to shut down.
Case Study Economic Analysis of Agriculture
rony is the nature of the economics of agriculture; even as many in America still
struggle with hunger, the government has been offering subsidies to the American
Ifarmer to artificially raise the price of produce, in some cases since 1933.
History of Subsidies
Because a typical farmer is so small compared to the entire market for the good he or she
offers, they cannot affect the price of the good, or try to affect the price of good too
efficaciously. Instead, they are referred to as ‘price takers’, who are forced to accept the
market price. However, subsidies alter this economic situation to occasionally illogical
results. At the end of World War I, farmers were rewarded by high prices as the government
Contd...
148 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY