Page 168 - DECO405_MANAGERIAL_ECONOMICS
P. 168
Unit 10: Imperfect Competition – Monopoly
2. Capital Costs: Certain businesses, such as international airlines and chemical Notes
companies, have relatively high set-up costs. In such cases the minimum efficient
scale of production might be very high indeed and this creates a formidable barrier
to entry.
3. Natural Factor Endowments: Sometimes firms, within a particular country, between
them control a major proportion of the world output of a commodity: nitrates from
Chile, coffee from Brazil and gold from South Africa are cases in point. A particular
country has a monopoly in the supply of a particular commodity due to natural
factor endowments and it is impossible to obtain supply of the commodity from
any other source.
4. Tariffs and Quotas: It can happen that a firm has a dominant position in its home
country, but faces competition internationally. A tariff raises the price of goods
imported into the domestic economy and a quota restricts the volume that can be
imported. They, therefore, protect domestic industry from international competition.
10.2 Price and Output Decisions
10.2.1 Short Run Equilibrium
In the short run the monopolist maximises his short run profits or minimises his short run losses
if the following two conditions are satisfied:
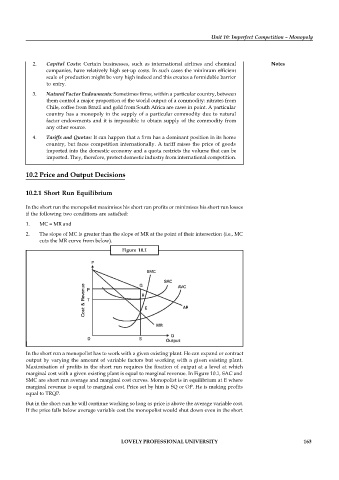
1. MC = MR and
2. The slope of MC is greater than the slope of MR at the point of their intersection (i.e., MC
cuts the MR curve from below).
Figure 10.1
In the short run a monopolist has to work with a given existing plant. He can expand or contract
output by varying the amount of variable factors but working with a given existing plant.
Maximisation of profits in the short run requires the fixation of output at a level at which
marginal cost with a given existing plant is equal to marginal revenue. In Figure 10.1, SAC and
SMC are short run average and marginal cost curves. Monopolist is in equilibrium at E where
marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost. Price set by him is SQ or OP. He is making profits
equal to TRQP.
But in the short run he will continue working so long as price is above the average variable cost.
If the price falls below average variable cost the monopolist would shut down even in the short
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 163