Page 65 - DECO405_MANAGERIAL_ECONOMICS
P. 65
Managerial Economics
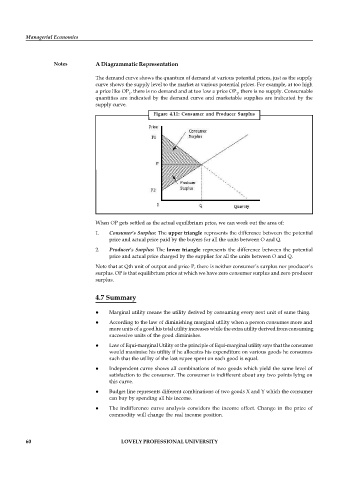
Notes A Diagrammatic Representation
The demand curve shows the quantum of demand at various potential prices, just as the supply
curve shows the supply level to the market at various potential prices. For example, at too high
a price like OP , there is no demand and at too low a price OP , there is no supply. Consumable
1 2
quantities are indicated by the demand curve and marketable supplies are indicated by the
supply curve.
Figure 4.11: Consumer and Producer Surplus
When OP gets settled as the actual equilibrium price, we can work out the area of:
1. Consumer’s Surplus: The upper triangle represents the difference between the potential
price and actual price paid by the buyers for all the units between O and Q.
2. Producer’s Surplus: The lower triangle represents the difference between the potential
price and actual price charged by the supplier for all the units between O and Q.
Note that at Qth unit of output and price P, there is neither consumer’s surplus nor producer’s
surplus. OP is that equilibrium price at which we have zero consumer surplus and zero producer
surplus.
4.7 Summary
Marginal utility means the utility derived by consuming every next unit of same thing.
According to the law of diminishing marginal utility when a person consumes more and
more units of a good his total utility increases while the extra utility derived from consuming
successive units of the good diminishes.
Law of Equi-marginal Utility or the principle of Equi-marginal utility says that the consumer
would maximise his utility if he allocates his expenditure on various goods he consumes
such that the utility of the last rupee spent on each good is equal.
Independent curve shows all combinations of two goods which yield the same level of
satisfaction to the consumer. The consumer is indifferent about any two points lying on
this curve.
Budget line represents different combinations of two goods X and Y which the consumer
can buy by spending all his income.
The indifference curve analysis considers the income effect. Change in the price of
commodity will change the real income position.
60 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY