Page 8 - DECO405_MANAGERIAL_ECONOMICS
P. 8
Unit 1: Introduction to Managerial Economics
Koontz and O'Donell define management as the creation and maintenance of an internal Notes
environment in an enterprise where individuals, working together in groups, can perform
efficiently and effectively towards the attainment of group goals. Thus, management is:
1. Coordination
2. An activity or an ongoing process
3. A purposive process
4. An art of getting things done by other people.
On the other hand, economics, in its broadest sense, is what economists do. Economists are
primarily engaged in analysing and providing answers to manifestations of the most fundamental
problem, scarcity. Scarcity of resources results from two fundamental facts of life:
1. Human wants are virtually unlimited and insatiable, and
2. Economic resources to satisfy these human demands are limited.
Thus, we cannot have everything we want; we must make choices broadly between three areas:
1. What to produce?
2. How to produce? and
3. For whom to produce?
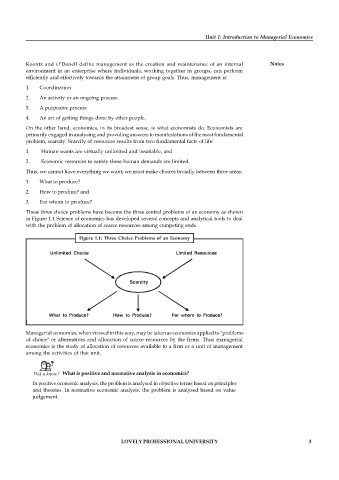
These three choice problems have become the three central problems of an economy as shown
in Figure 1.1 Science of economics has developed several concepts and analytical tools to deal
with the problem of allocation of scarce resources among competing ends.
Figure 1.1: Three Choice Problems of an Economy
Managerial economics, when viewed in this way, may be taken as economics applied to "problems
of choice" or alternatives and allocation of scarce resources by the firms. Thus managerial
economics is the study of allocation of resources available to a firm or a unit of management
among the activities of that unit.
Did u know? What is positive and normative analysis in economics?
In positive economic analysis, the problem is analysed in objective terms based on principles
and theories. In normative economic analysis, the problem is analysed based on value
judgement.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 3