Page 283 - DMGT405_FINANCIAL%20MANAGEMENT
P. 283
Unit 13: Management of Cash
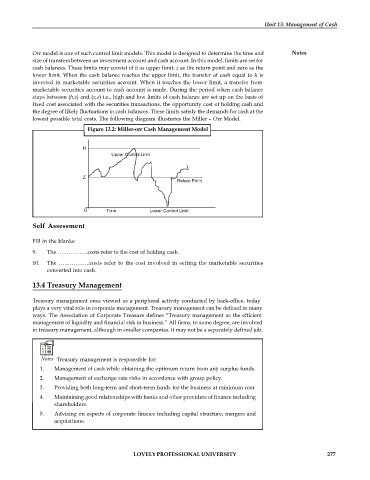
Orr model is one of such control limit models. This model is designed to determine the time and Notes
size of transfers between an investment account and cash account. In this model, limits are set for
cash balances. These limits may consist of h as upper limit, z as the return point and zero as the
lower limit. When the cash balance reaches the upper limit, the transfer of cash equal to h is
invested in marketable securities account. When it touches the lower limit, a transfer from
marketable securities account to cash account is made. During the period when cash balance
stays between (h,z) and (z,o) i.e., high and low limits of cash balance are set up on the basis of
fixed cost associated with the securities transactions, the opportunity cost of holding cash and
the degree of likely fluctuations in cash balances. These limits satisfy the demands for cash at the
lowest possible total costs. The following diagram illustrates the Miller – Orr Model.
Figure 13.2: Miller-orr Cash Management Model
H
Upper Control Limit
Z
Return Point
O Time Lower Control Limit
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
9. The ……………..costs refer to the cost of holding cash.
10. The ……………..costs refer to the cost involved in setting the marketable securities
converted into cash.
13.4 Treasury Management
Treasury management once viewed as a peripheral activity conducted by back-office, today
plays a very vital role in corporate management. Treasury management can be defined in many
ways. The Association of Corporate Treasure defines “Treasury management as the efficient
management of liquidity and financial risk in business.” All firms, to some degree, are involved
in treasury management, although in smaller companies, it may not be a separately defined job.
Notes Treasury management is responsible for:
1. Management of cash while obtaining the optimum return from any surplus funds.
2. Management of exchange rate risks in accordance with group policy.
3. Providing both long-term and short-term funds for the business at minimum cost.
4. Maintaining good relationships with banks and other providers of finance including
shareholders.
5. Advising on aspects of corporate finance including capital structure, mergers and
acquisitions.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 277