Page 265 - DMGT404 RESEARCH_METHODOLOGY
P. 265
Unit 12: Hypothesis Testing
Parametric tests are of following types: Notes
12.3.1 One Sample Test
One sample tests can be categorized into 2 categories.
z Test
1. When sample size is > 30
P = Proportion in sample 1
1
P = Proportion in sample 2
2
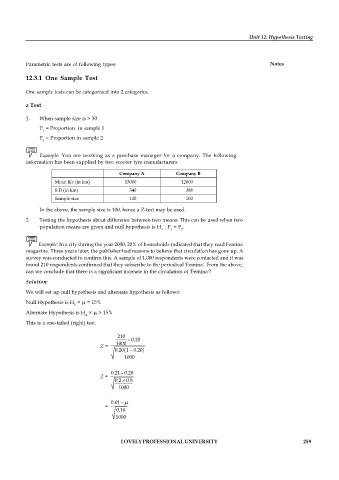
Example: You are working as a purchase manager for a company. The following
information has been supplied by two scooter tyre manufacturers.
Company A Company B
Mean life (in km) 13000 12000
S.D (in km) 340 388
Sample size 100 100
In the above, the sample size is 100, hence a Z-test may be used.
2. Testing the hypothesis about difference between two means: This can be used when two
population means are given and null hypothesis is H : P = P .
o 1 2
Example: In a city during the year 2000, 20% of households indicated that they read Femina
magazine. Three years later, the publisher had reasons to believe that circulation has gone up. A
survey was conducted to confirm this. A sample of 1,000 respondents were contacted and it was
found 210 respondents confirmed that they subscribe to the periodical 'Femina'. From the above,
can we conclude that there is a significant increase in the circulation of 'Femina'?
Solution:
We will set up null hypothesis and alternate hypothesis as follows:
Null Hypothesis is H × m = 15%
0
Alternate Hypothesis is H × m > 15%
A
This is a one-tailed (right) test.
210
– 0.20
1000
Z =
0.20 (1 0.20- )
1000
0.21 – 0.20
Z =
´
0.2 0.8
1000
0.01 – m
=
0.16
1000
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 259