Page 266 - DMGT404 RESEARCH_METHODOLOGY
P. 266
Research Methodology
Notes
0.1
=
0.4
31.62
0.1
= = 8.33
0.012
As the value of Z at 0.05 =1.64 and calculated value of Z falls in the rejection region, we reject null
hypothesis, and therefore we conclude that the sale of 'Femina' has increased significantly.
T-test (Parametric Test)
T-test is used in the following circumstances: When the sample size n < 30.
Example:
1. A certain pesticide is packed into bags by a machine. A random sample of 10 bags are
drawn and their contents are found as follows: 50, 49, 52, 44, 45, 48, 46, 45, 49, 45. Confirm
whether the average packaging can be taken to be 50 kgs.
In this text, the sample size is less than 30. Standard deviations are not known using this
test. We can find out if there is any significant difference between the two means i.e.
whether the two population means are equal.
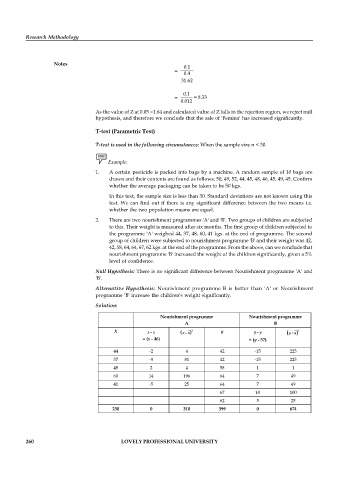
2. There are two nourishment programmes 'A' and 'B'. Two groups of children are subjected
to this. Their weight is measured after six months. The first group of children subjected to
the programme 'A' weighed 44, 37, 48, 60, 41 kgs. at the end of programme. The second
group of children were subjected to nourishment programme 'B' and their weight was 42,
42, 58, 64, 64, 67, 62 kgs. at the end of the programme. From the above, can we conclude that
nourishment programme 'B' increased the weight of the children significantly, given a 5%
level of confidence.
Null Hypothesis: There is no significant difference between Nourishment programme 'A' and
'B'.
Alternative Hypothesis: Nourishment programme B is better than 'A' or Nourishment
programme 'B' increase the children's weight significantly.
Solution:
Nourishment programme Nourishment programme
A B
X x – x ( –x x ) 2 y y – y ( –y y ) 2
= (x - 46) = (y - 57)
44 -2 4 42 -15 225
37 -9 81 42 -15 225
48 2 4 58 1 1
60 14 196 64 7 49
41 -5 25 64 7 49
67 10 100
62 5 25
230 0 310 399 0 674
260 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY