Page 289 - DMGT404 RESEARCH_METHODOLOGY
P. 289
Unit 13: Multivariate Analysis
2. The fact that a regression coefficient is independent of change of origin can also be Notes
utilised to further simplify the computational work.
3. The regression coefficients of equations (2) and (3) can be written by symmetry as
given below:
(å x x )(å x - x x )(å x x )
) (å
2
b = 2 1 3 2 3 2 1 3
) (å
21.3 (å x 2 1 )(å x - x x )
2
1 3
3
) (å
(å x x )(å x - x x )(å x x )
2
b = 2 3 1 2 1 1 3
) (å
23.1 (å x 2 1 )(å x - x x ) 2
2
3
1 3
Further, b = b and b = b and the expressions for the constant terms are
31.2 13.2 32.1 23.1
a = X - b X - b X and a = X - b X - b X respectively.
2.13 2 21.3 1 23.1 3 3.12 3 31.2 1 32.1 2
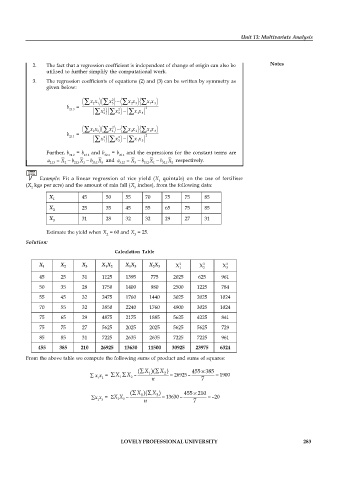
Example: Fit a linear regression of rice yield (X quintals) on the use of fertiliser
1
(X kgs per acre) and the amount of rain fall (X inches), from the following data:
2 3
X 45 50 55 70 75 75 85
1
X 25 35 45 55 65 75 85
2
X 31 28 32 32 29 27 31
3
Estimate the yield when X = 60 and X = 25.
2 3
Solution:
Calculation Table
X X X X X X X X X X X X
2
2
2
3
1
3
2
3
2
1
1
2
1
2
3
45 25 31 1125 1395 775 2025 625 961
50 35 28 1750 1400 980 2500 1225 784
55 45 32 2475 1760 1440 3025 2025 1024
70 55 32 3850 2240 1760 4900 3025 1024
75 65 29 4875 2175 1885 5625 4225 841
75 75 27 5625 2025 2025 5625 5625 729
85 85 31 7225 2635 2635 7225 7225 961
455 385 210 26925 13630 11500 30925 23975 6324
From the above table we compute the following sums of product and sums of squares:
´
å
å
å x x = å X å X – ( X 1 )( X 2 ) = 26925 – 455 385 = 1900
1 2 1 2 n 7
å
å
´
( X )( X ) 455 210
åx x = S X X – 1 3 = 13630 – = –20
1 3 1 3 n 7
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 283