Page 73 - DMGT404 RESEARCH_METHODOLOGY
P. 73
Unit 4: Sampling Design
Notes
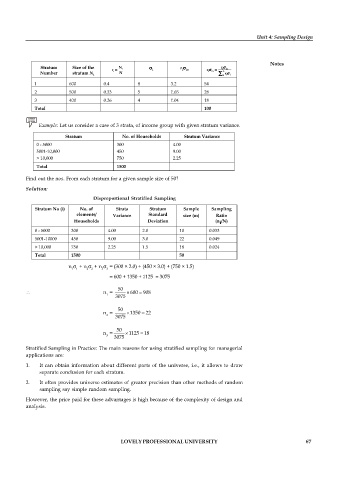
Stratum Size of the i r = N i i r i r in = i r in
i in
Number stratum N i N å 3 1 i r i
1 600 0.4 8 3.2 54
2 500 0.33 5 1.65 28
3 400 0.26 4 1.04 18
Total 100
Example: Let us consider a case of 3 strata, of income group with given stratum variance.
Stratum No. of Households Stratum Variance
0 - 5000 300 4.00
5001-10,000 450 9.00
> 10,000 750 2.25
Total 1500
Find out the nos. From each stratum for a given sample size of 50?
Solution:
Disproportional Stratified Sampling
Stratum No (i) No. of Strata Stratum Sample Sampling
elements/ Variance Standard size (m) Ratio
Households Deviation (n /N)
i
0 - 5000 300 4.00 2.0 10 0.033
5001-10000 450 9.00 3.0 22 0.049
> 10,000 750 2.25 1.5 18 0.024
Total 1500 50
n + n + n = (300 × 2.0) + (450 × 3.0) + (750 × 1.5)
1 1 2 2 3 3
= 600 + 1350 + 1125 = 3075
50
n = 600 908
1
3075
50
n = 1350 22
2
3075
50
n = 1125 18
3
3075
Stratified Sampling in Practice: The main reasons for using stratified sampling for managerial
applications are:
1. It can obtain information about different parts of the universe, i.e., it allows to draw
separate conclusion for each stratum.
2. It often provides universe estimates of greater precision than other methods of random
sampling say simple random sampling.
However, the price paid for these advantages is high because of the complexity of design and
analysis.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 67